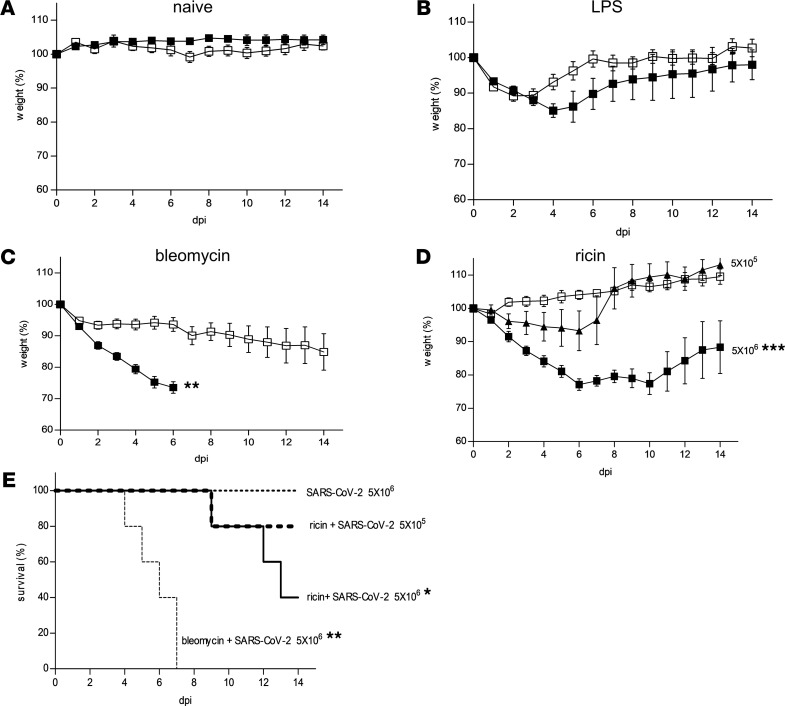
Figure 1. Effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on body weight and mortality of CD-1 mice pretreated with ALI/ARDS stimulants.
(A–D) Body weights of CD-1 mice (presented as percentage of original weight determined at the time of viral instillation) were monitored over a period of 15 days after i.n. instillation of SARS-CoV-2. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 5–6 per group, analyzed using 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s posttests, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with no virus. Displayed representative experiment out of 3–5 independent experiments for each treatment. (A) Body weights of mice infected with virus at a dose of 5 × 106 PFU per mouse (black squares) compared with body weights of naive mice (white squares). (B) Mice were administered LPS (1.7 mg/ kg body weight) and 1 day later were infected (black squares) or not (white squares) with virus (5 × 106 PFU/mouse). (C) Mice were administered bleomycin (2 U/kg body weight) and 4 days later were infected (black squares) or not (white squares) with virus (5 × 106 PFU/mouse). Because of significant mortality, only data of 0 to 6 days are presented for bleomycin–SARS-CoV-2 mice. (D) Mice were administered ricin (1.7 μg/ kg body weight) and 2 days later were infected with virus at a dose of 5 × 105 (black triangles) or 5 × 106 (black squares) PFU/mouse or not (white squares). (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of the mouse groups exhibiting mortality: dotted line is SARS-CoV-2 (5 × 106 PFU/mouse), thick dashed line is LDR–SARS-CoV-2 (5 × 105 PFU/mouse), black line is LDR–SARS-CoV-2 (5 × 106 PFU/mouse), thin dashed line is bleomycin–SARS-CoV-2 (5 × 106 PFU/mouse). Data were analyzed using log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. n = 5.