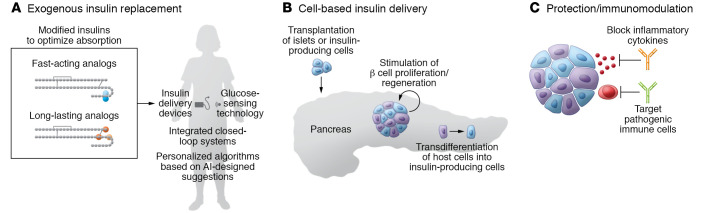
Figure 3. Emerging or future T1D therapies.
(A) Exogenous insulin replacement includes insulin analogs designed to optimize absorption, integrated closed-loop systems combining insulin delivery devices and glucose-sensing technology, and personalized algorithms (AI, artificial intelligence) to tailor insulin replacement. (B) Cell-based insulin delivery options include transplantation of islets or insulin-producing cells (derived from ES or iPS cells), strategies to stimulate β cell proliferation or regeneration, and approaches that encourage transdifferentiation of host cells into insulin-producing cells. (C) Protective strategies include immunomodulatory approaches to block inflammatory cytokines or pathogenic immune cells and prevent damage or loss of β cells. See text for additional information.