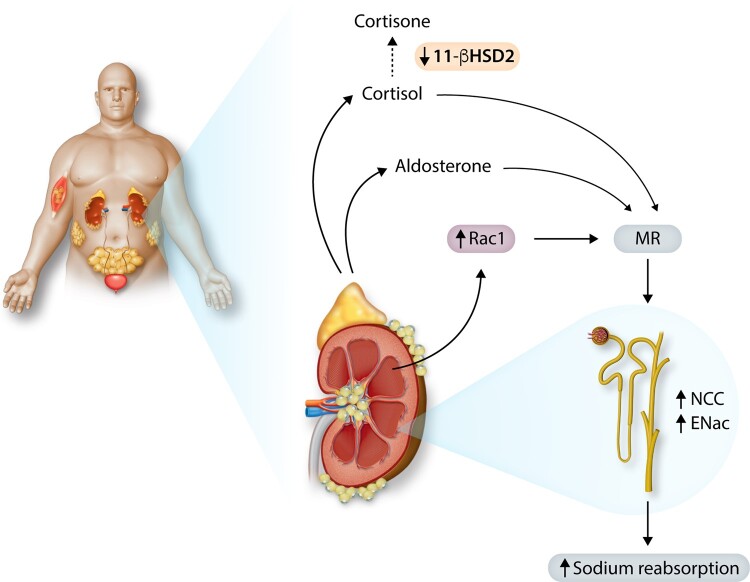
Figure 3.
Possible mechanisms of renal tubular mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) activation, increased renal sodium reabsorption, and hypertension in obesity. Obesity increases angiotensin II which stimulates secretion of aldosterone, normally the primary agonist of renal tubular MR. Adipokines, such as leptin, may also stimulate aldosterone secretion and obesity may cause MR activation via aldosterone-independent mechanisms such as increased renal tubular expression of Rac 1, a small GTP-binding protein member of the Rho family of GTPases. Cortisol may also activate MR in obesity via down-regulation of 11β-HSD2, which normally converts cortisol to cortisone, a glucocorticoid that does not avidly bind MR.