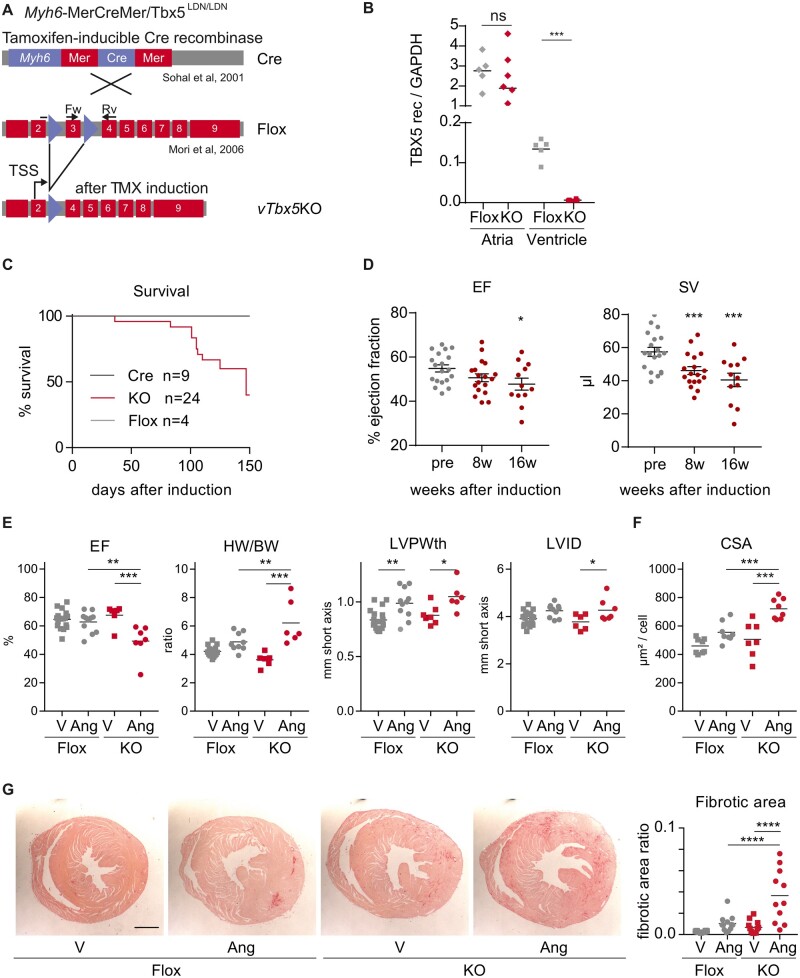
Figure 2.
Characterization of vTbx5KO mice cardiac function under basal and stress conditions. (A) Mating scheme for vTbx5KO mouse generation by mating Myh6-MerCreMer10 and TBX5LDN/LDN9 mice. (B) RT-(q)PCR analysis of TBX5 recombination in the ventricles and in the atria (Flox n = 5; KO = 6 biological replicates). (C) Survival curve of vTbx5KO mice shows significantly reduced lifespan as compared to control mice (Cre n = 9; Flox n = 4; KO n = 24 biological replicates). (D) vTbx5KO shows cardiac dysfunction with mildly reduced EF and SV decrease 16 weeks post-recombination (KO pre n = 19, 8w n = 18, 16w n = 12 biological replicates: the animal number decreased due to SCD). (E) Angiotensin (Ang) II-treated vTbx5KO mice show exacerbated cardiac function (EF), hypertrophic remodelling (HW/BW; heart weight/body weight, LVPWth; left ventricular posterior wall thickness) and decompensation (LVIDd; left ventricular inner diameter in diastole) as compared to Ang II-treated Flox mice (Flox vehicle n = 19; Flox Ang n = 11; KO vehicle n = 7; KO Ang n = 7 biological replicates). (F) CM Cross-sectional cell area (CSA) is increased in Ang II-treated vTbx5KO mice compared to Ang-Flox mice (Flox vehicle n = 19; Flox Ang n = 11; KO vehicle n = 12; KO Ang n = 11 biological replicates). (G) Collagen staining with picrosirius red shows that Ang II-induced fibrosis is exacerbated in vTbx5KO vs. Flox mice. Scale bar: 1 mm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by (B) one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison post hoc test; (C) log-rank test (Mantel–Cox); (D–F) paired t-tests; (G) One-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparison post hoc test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.