Figure 7.
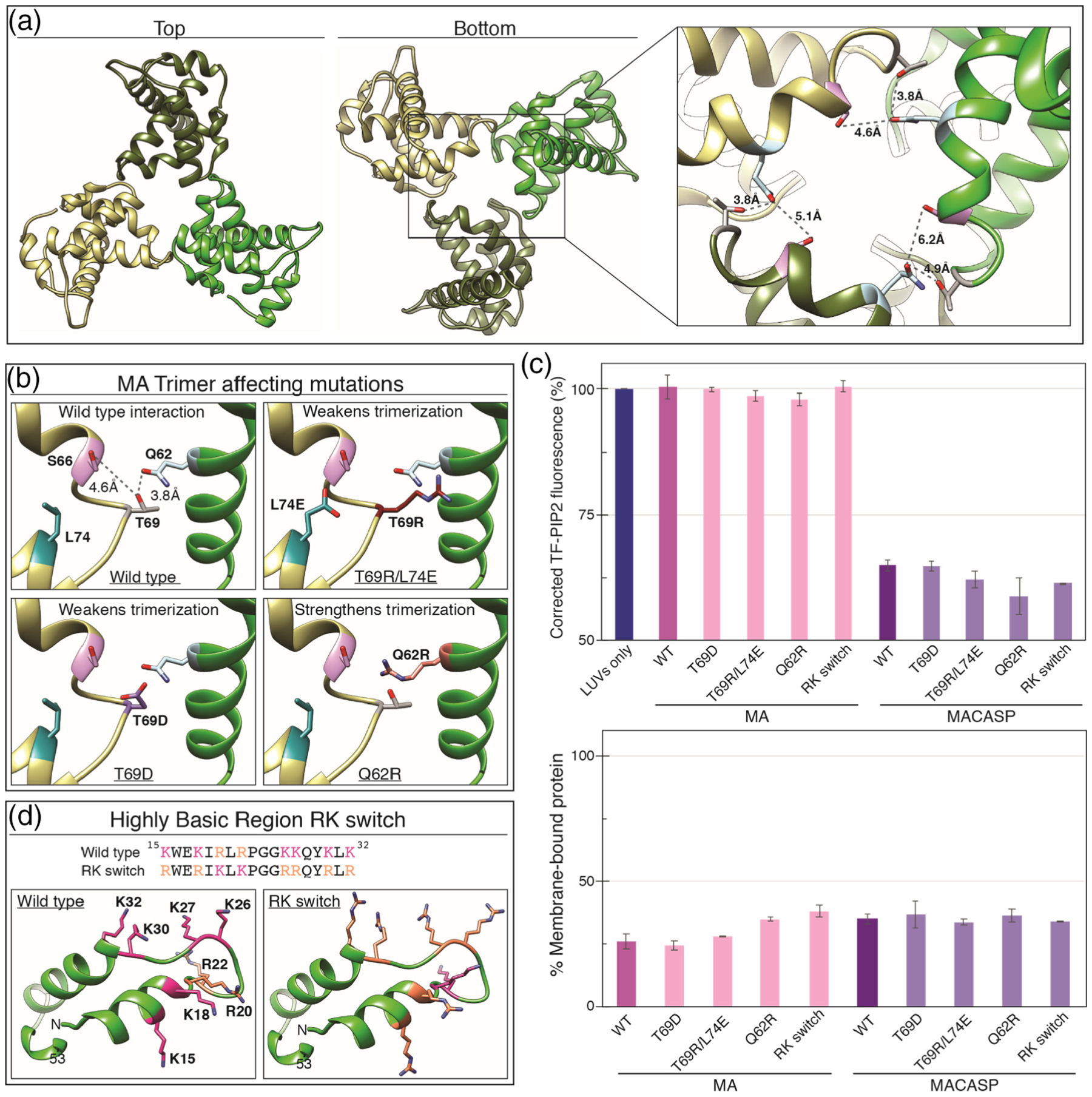
PIP2 clustering is not affected by mutations that weaken MA trimerization or alter charged residue type. (a) HIV-1 MA trimer (PDB 1HIW [90]) top and bottom views. Inset shows side-chains of known trimer interacting residues Q62 (blue), S66 (pink), T69 (grey) and Q62 (blue). (b) Mutations in MA that weaken or strengthen trimerization. (c) (Top) Effect of MA trimer mutations and RK switch mutant on PIP2 quenching in the context of MA and MACASP proteins. (Bottom) Percent of total protein associated with membranes. (d) Highly basic surface of the HIV-1 membrane binding domain. All basic amino acid side-chains are shown as pink (K) or orange (R). In the RK switch mutant, each K residue has been mutated to R and each R residue has been mutated to K.
