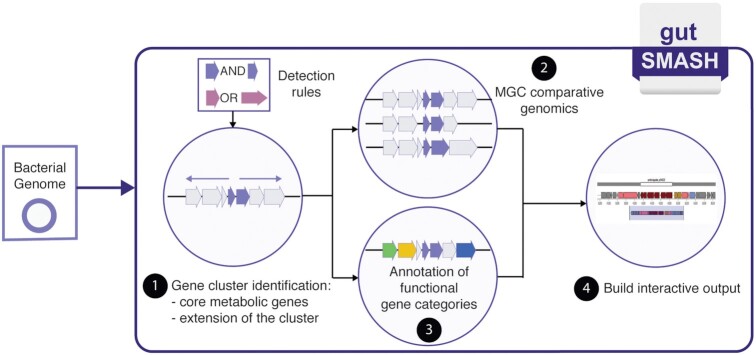
Figure 1.
Overall workflow of the gutSMASH web server. gutSMASH takes a bacterial genome sequence as input either in GenBank, EMBL or FASTA format. First, the program iterates over the detection rules to identify the gene clusters. Next, if enabled, the predicted MGCs are compared to the databases specified to evaluate the similarity to any known pathways, or to assess the similarity to gene clusters that were predicted by gutSMASH from publicly available whole-genome sequences.