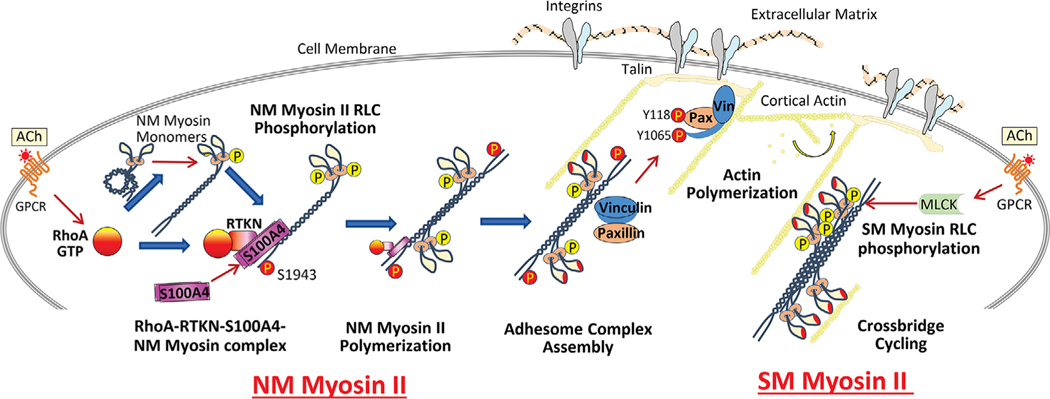
Figure 7. Model for proposed role of S100A4 in the regulation of NM myosin II filament assembly and contractile tension development in airway SM.
The activation of RhoA GTPase by ACh catalyses the binding of S100A4 to the C-terminal heavy chain of assembly-competent NM myosin II monomers at the cell cortex via the RhoA GTP-binding protein, rhotekin. S100A4 binding facilitates the polymerization of NM myosin II monomers into filaments. RhoA also regulates the phosphorylation of the RLC of NM myosin II, which promotes the assembly-competent conformation of NM myosin II and also activates actin-activated cross-bridge cycling by NM myosin II filaments. Cross-bridge cycling by NM myosin II provides the motor for the recruitment of the adhesome proteins vinculin and paxillin to integrin-associated adhesome complexes at the membrane. Signalling pathways activated by these complexes regulate cortical actin polymerization, which is necessary for tension generation. Concurrently, the activation of cross-bridge cycling by SM myosin II regulates tension generation by the SM contractile apparatus.