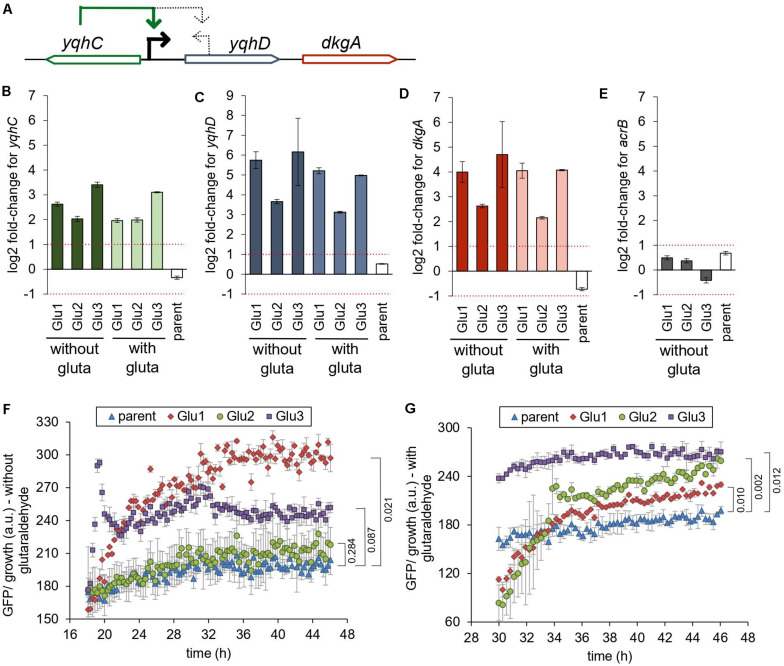
FIGURE 3.
Mutations in yqhC are associated with upregulation of yqhC, yqhD, and dkgA. (A) The transcriptional regulator yqhC activates the aldehyde reductase yqhD and the methylglyoxal reductase dkgA genes (Lee et al., 2010; Turner et al., 2011). (B–E) RT-qPCR results for (B) yqhC (C) yqhD, (D) dkgA, and (E) acrB expression for the strains evolved in glutaraldehyde, compared to the parent (non-evolved) strain, when grown in the presence or absence of glutaraldehyde. The column “parent” denotes the log2 fold-change between the parent strain in media containing glutaraldehyde compared to media without the biocide. The gene acrB was used as a negative control (less than twofold change between evolved and non-evolved strains). The experiments were performed in duplicate, and the error was calculated as described in “Materials and Methods” section (F,G). Expression of GFP under the control of the yqhC predicted promoter in each of the indicated strains. (F) Minimal media without glutaraldehyde (G) Minimal media with glutaraldehyde. The experiments were performed in duplicate, and the standard error was calculated. The p-values (one-tailed t-test for independent means) for the last time point collected are indicated. gluta refers to glutaraldehyde.