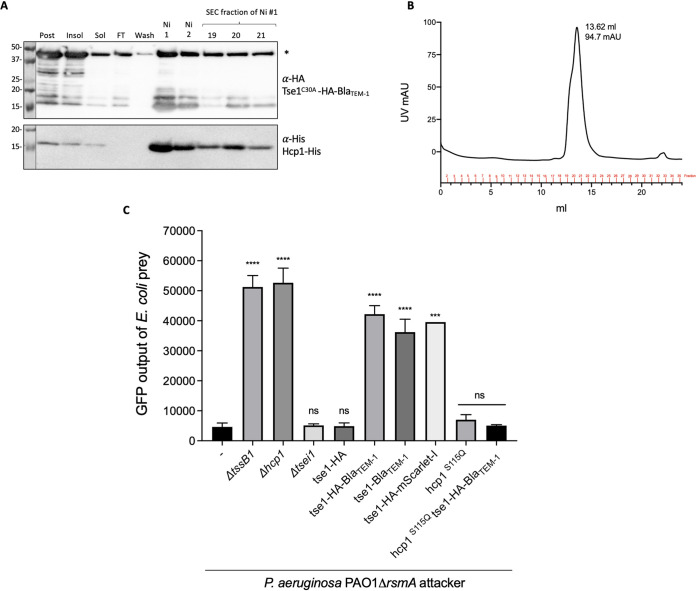
FIG 6.
Large Tse1 chimera can bind Hcp1 but block H1-T6SS-dependent killing. (A) Western blot of Hcp1-His and Tse1C30A-HA-BlaTEM-1 copurification; lanes labeled on the top are postexpression sample, insoluble and soluble samples after sonication and clarification, flowthrough (FT) from the Ni-NTA column, wash fraction before elution, Ni fractions corresponding to the elution peak, and SEC fractions corresponding to the gel filtration peak. The antibodies used are labeled on the right: top, anti-HA antibody (BioLegend) at 1:1,000 concentration; bottom, anti-His antibody (GenScript) at 1:1000 concentration. Molecular weight standards are on the left. Asterisk denotes the correct size of Tse1C30A-HA-BlaTEM-1 at 46.4 kDa. (B) SEC chromatograph of purified Hcp1-His and Tse1C30A-HA-BlaTEM-1. (C) Competition assay of P. aeruginosa PAO1 ΔrsmA attackers against E. coli-GFP prey after a 13-h competition. GFP output represents the number of E. coli cells in the sample. Statistical testing was conducted by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple-comparison test and family-wise significance and confidence level set to P = 0.05; each strain compared to parental P. aeruginosa PAO1 ΔrsmA strain. ****, P < 0.0001; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant. Mean and SEMs of n biological replicates: n = 6, 6, 4, 6, 6, 6, 6, 1, 3, and 3, in order of strains.