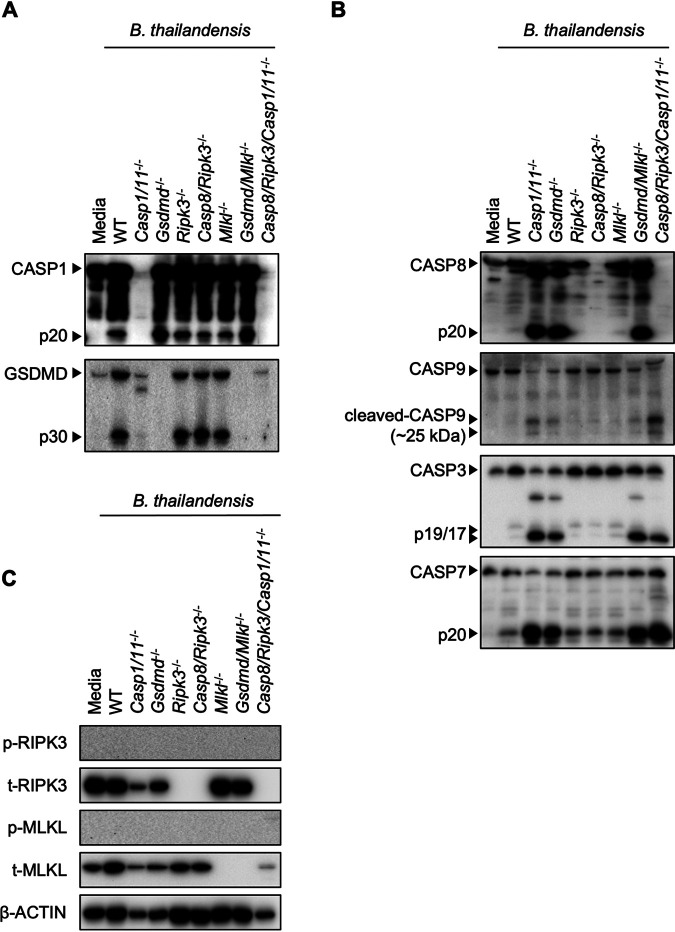
FIG 2.
B. thailandensis infection induces pyroptotic and apoptotic cell death in BMDMs. (A to C) Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were infected with B. thailandensis and combined cell and supernatant lysates (for caspase and gasdermin D [GSDMD] blots) or cell lysates were collected at 24 h postinfection. Immunoblots were performed to detect pyroptosis activation, indicated by cleavage of caspase-1 (CASP1) and GSDMD (A), apoptosis activation, indicated by cleavage of caspase-8 (CASP8), caspase-9 (CASP9), caspase-3 (CASP3), and caspase-7 (CASP7) (B), or necroptosis activation, indicated by phosphorylation of RIPK3 (p-RIPK3) and MLKL (p-MLKL) (C). Data are representative of one of at least three independent biological experiments, and BMDMs used to generate data in Fig. 2 were also used to generate data presented in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material and Fig. 3B to D.