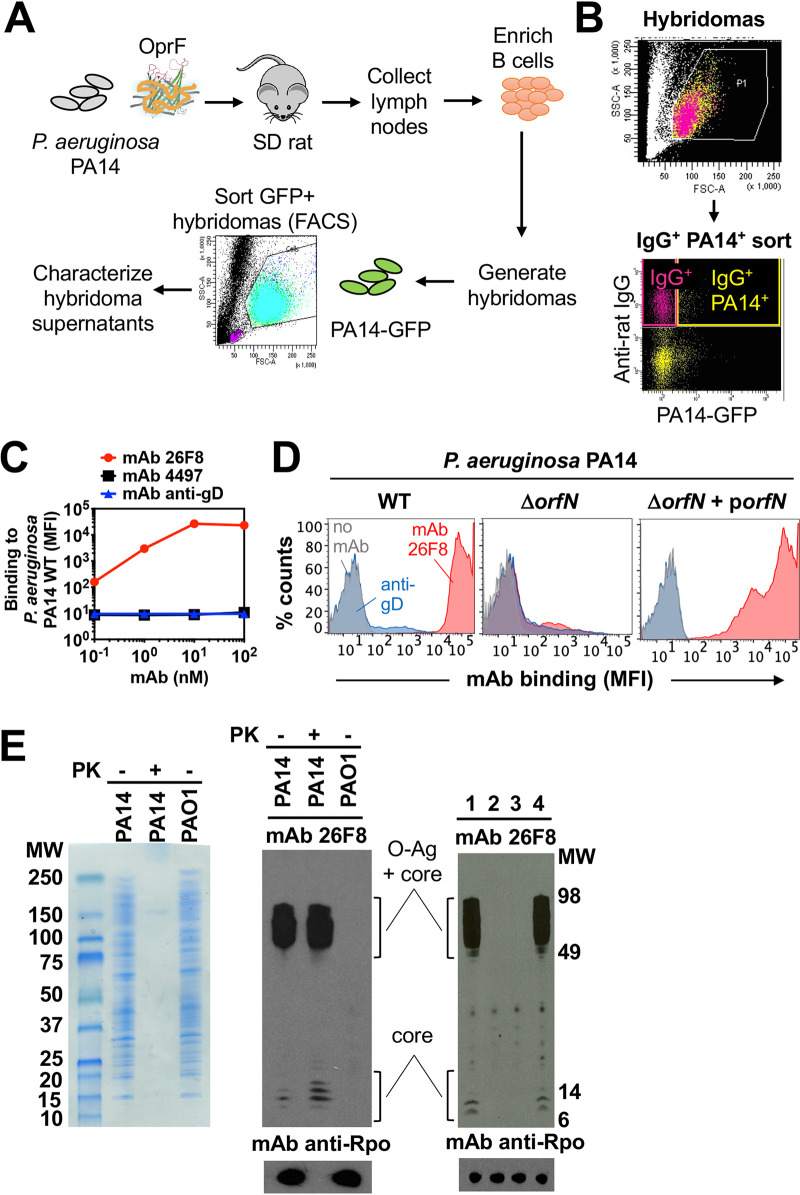
FIG 1.
Generation and characterization of MAb 26F8 recognizing LPS O antigen on P. aeruginosa bacteria. (A) Schematic of the immunization and sorting procedure. Rats were immunized with P. aeruginosa PA14 bacteria and boosted with OprF beta-barrel protein reconstituted in amphipols. Rat lymph nodes were harvested, and purified B cells were fused with Sp2ab cells to generate hybridomas, which were subjected to fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) based on binding to GFP-labeled P. aeruginosa PA14. Supernatants were purified, and clones were selected based on positive binding to whole P. aeruginosa bacteria, as determined by FACS. (B) FACS sorting profile of rat hybridomas to select P. aeruginosa-binding antibodies. Rat hybridoma cells were incubated with fluorescent anti-rat IgG antibodies and with P. aeruginosa PA14 bacteria expressing GFP and were sorted from the IgG+ PA14+ gate (yellow; upper right quadrant). (C) Intact P. aeruginosa PA14 WT bacteria were incubated with MAbs and fluorescently labeled anti-human secondary antibodies, followed by determination of the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI; arbitrary units) by flow cytometry. Rat MAb 26F8, engineered with human Fc (red circles), showed dose-dependent, high-intensity binding to P. aeruginosa. Binding was hardly detectable for isotype-matched anti-S. aureus MAb 4497 (black squares) or for MAb against cytomegalovirus gD (anti-gD; blue triangles). (D) MAb 26F8 demonstrated high-intensity binding to intact P. aeruginosa PA14 WT bacteria (left). MAb 26F8 did not show binding to PA14 ΔorfN bacteria, which lack LPS O antigen (middle). Binding of MAb 26F8 to PA14 ΔorfN was restored by complementation with pUCP19-orfN (porfN) plasmid (right). Binding of MAb 26F8 to PA14 WT was represented by a shift in fluorescence of approximately 3 log compared to background fluorescence without antibody. Antibody binding was assessed by flow cytometry and was expressed as MFI. Red, MAb 26F8; blue, MAb anti-gD; gray, no MAb; MAbs were incubated at 10 nM. (E) (Left) Whole-cell lysates of P. aeruginosa PA14 WT or PAO1 WT were treated with or without proteinase K (PK), separated on SDS-PAGE gels, and stained with Coomassie. (Middle) Lysates of P. aeruginosa strains PA14 WT and PAO1 WT, treated with or without PK, were immunoblotted with MAb 26F8 (top) or, as a protein loading control, with MAb anti-RNA polymerase-α (Rpo) (bottom). (Right) Lysates of P. aeruginosa PA14 WT (lane 1), ΔorfN (lane 2), ΔorfN plus empty pUCP19 plasmid (lane 3), or ΔorfN plus pUCP19-orfN (lane 4) were immunoblotted with MAb 26F8 (top) or, as a loading control, with anti-Rpo MAb (bottom). MW, molecular weight marker.