FIG 5.
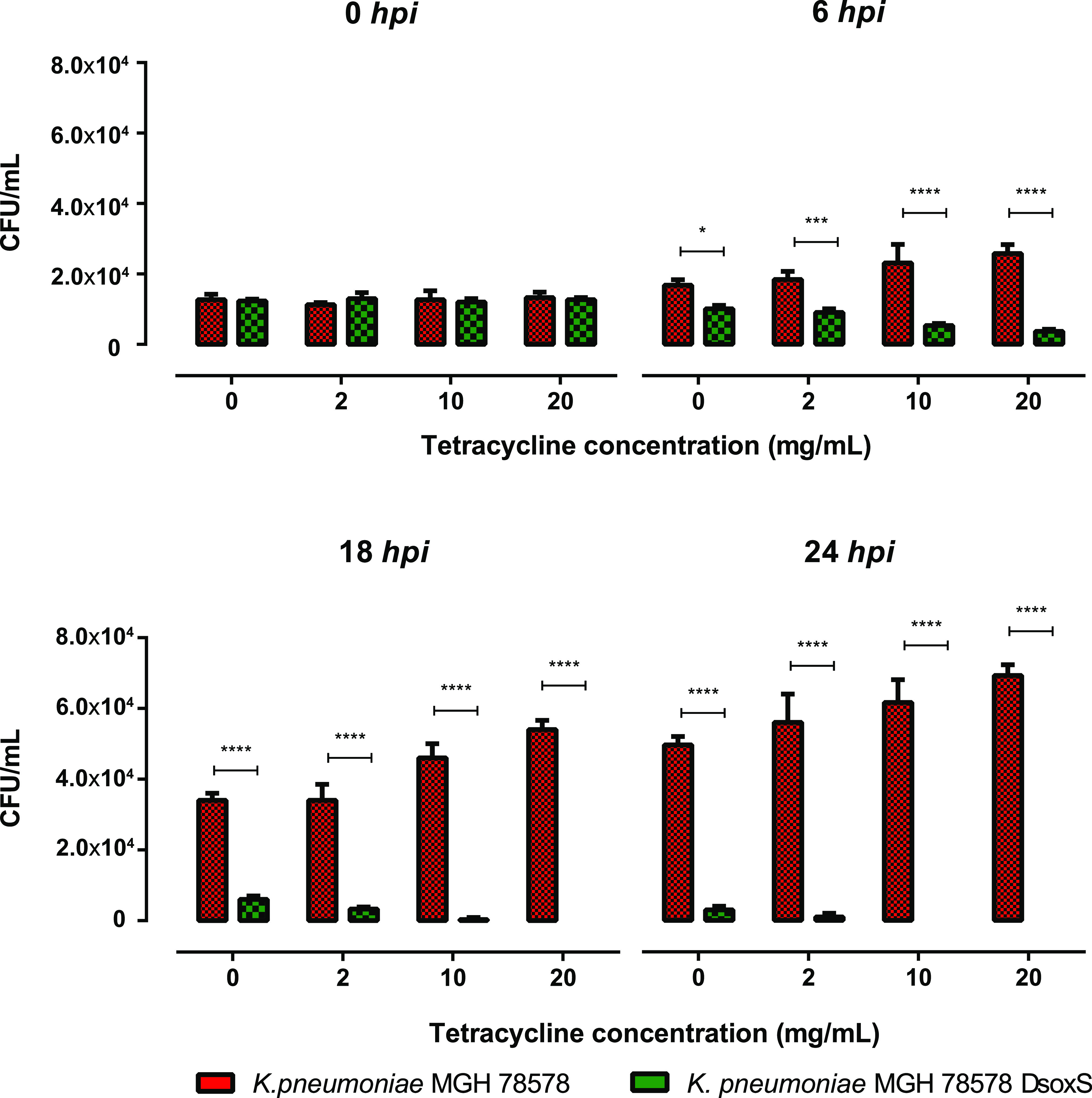
Survival of bacteria in a zebrafish larvae infection model where the larvae are treated with tetracycline. Tetracycline induces ROS generation in the zebrafish larvae. The bar charts show the survival of the different bacterial cultures in the larval blood at 0, 6, 18, and 24 h postinfection and at different concentrations of tetracycline. Error bars represent standard deviations (SD) calculated from 3 independent reads. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA and Sidak's multiple-comparison test, comparing the different tetracycline concentrations with the control group for each time point.
