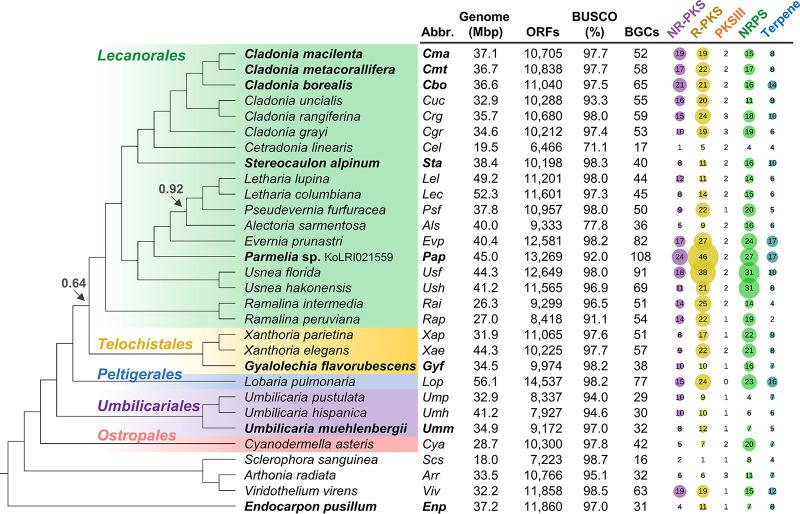
FIG 1.
Genome-encoded metabolic potentials of lichens. A coalescent-based species tree is reconstructed for 29 lichen-forming fungi and Cyanodermella asteris (a plant endophyte). The tree is rooted to Endocarpon pusillum. All local posterior probabilities for nodal supports are higher than 0.98, except those marked by arrows. The five orders of the Lecanoromycetes are highlighted with different colors, and lichen genomes sequenced by the Korean Lichen Research Institute are marked in boldface. BUSCO describes the completeness of the genome assemblies. The numbers of biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) are predicted by antiSMASH, and bubble plots indicate the relative abundance of core biosynthetic enzyme categories. NR-PKS, nonreducing type I PKS; R-PKS, reducing type I PKS (including PKS-NRPS hybrid enzymes); PKSIII, type III PKS; NRPS, nonribosomal peptide synthetase (including NRPS-like enzymes); and Terpene, biosynthetic enzymes related to terpenoid production.