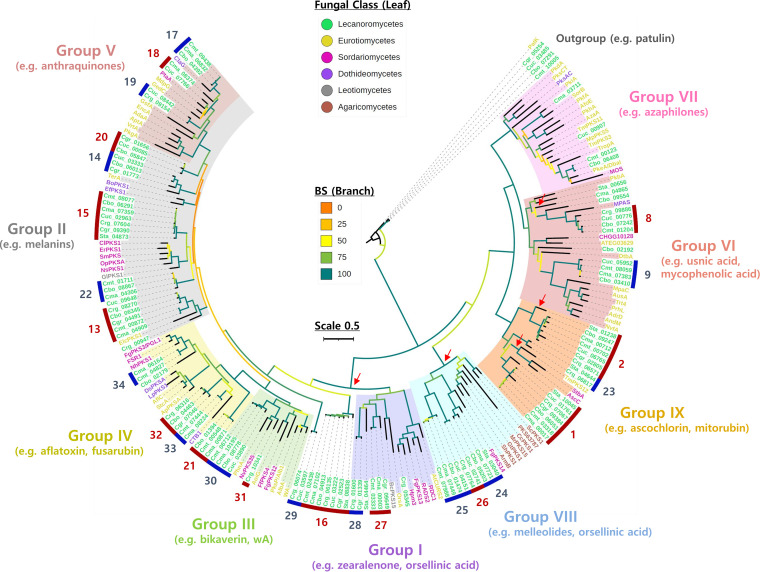
FIG 5.
The ninth clade of fungal nonreducing PKS genes. A maximum likelihood tree of 103 NR-PKSs in the six Cladonia spp. and Stereocaulon alpinum and 82 NR-PKSs linked to known compounds in nonlichenized fungi was reconstructed using concatenated sequences of ketosynthase and product template domains. The outgroup was set to 6-methylsalicylic acid synthases (6MSAS) found in Cladonia spp. and the 6MSAS for the patulin biosynthesis in Penicillium expansum. Branches are color coded, based on bootstrap (BS) values. The scale represents 0.5 amino acid sequence substitution per site. Blue and red strips with associated numbers at the outermost region indicate PKS families identified by the gene cluster network analysis (Fig. 2). Phylogenetic clades representing nine NR-PKS groups (groups I to IX) are shaded with different colors. The NR-PKS groups are supported by BS values greater than 75, except for group II. Note that the newly identified NR-PKS group (group IX) includes the PKS1, PKS2, and PKS23 families, candidate PKSs for cortical and medullary substances of lichens. Red arrows indicate polyphyletic losses of the C-methyltransferase domain of NR-PKSs.