FIG 1.
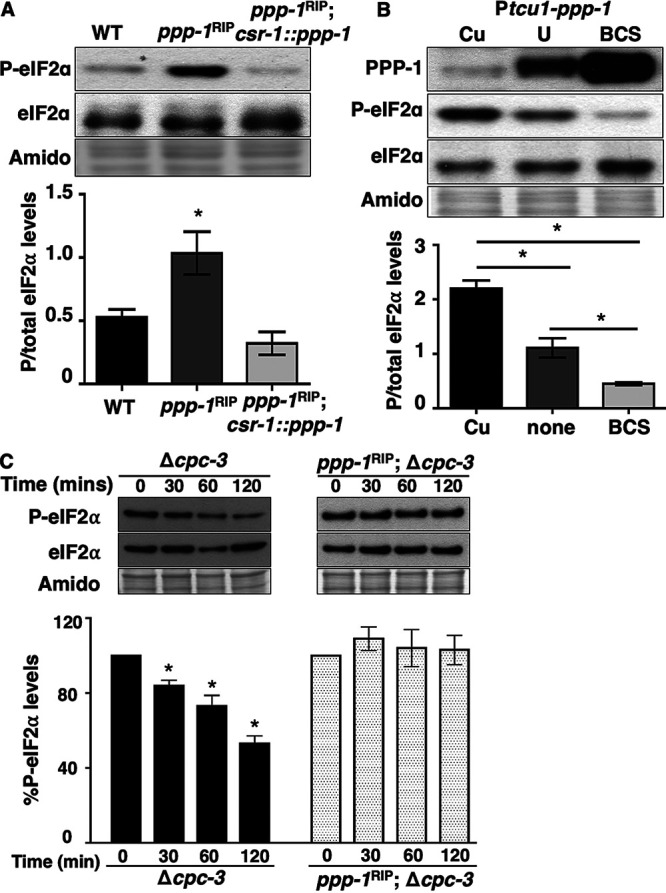
PPP-1 phosphatase reduces P-eIF2α levels and is critical for dephosphorylation of P-eIF2α in vitro. (A) Western blot of protein extracted from WT, ppp-1RIP mutant, and ppp-1RIP; csr1::ppp-1 complemented strains during the subjective night (DD28) and probed with anti-P-eIF2α and total eIF2α antibodies. The P-eIF2α/total eIF2α signal is plotted below for each strain (mean ± the SEM, n = 3; *, P < 0.05 [Student's t-test]). (B) Western blot of protein from Ptcu1-ppp-1 cells grown in the presence of copper sulfate (Cu), BCS, or untreated (U); harvested at DD28; and probed with anti-PPP-1, anti-P-eIF2α, and anti-eIF2α antibodies. The graph below shows the average signal of P-eIF2α/total eIF2α (mean ± the SEM, n = 3; *, P < 0.05 [Student's t-test]). (C) In vitro dephosphorylation assay using cell extracts from Δcpc-3 and ppp-1RIP; Δcpc-3 cells incubated with P-eIF2α from eIF2γ::v5 cells for 0, 30, 60, or 120 min. P-eIF2α and total eIF2α levels were examined by Western blotting. The graph below shows the average signal of P-eIF2α normalized to total protein for each time point and normalized to the value at time zero (mean ± the SEM, n = 4; *, P < 0.05 [Student's t-test compared to time zero]). In panels A to C, membranes were stained with amido black as a protein loading control.
