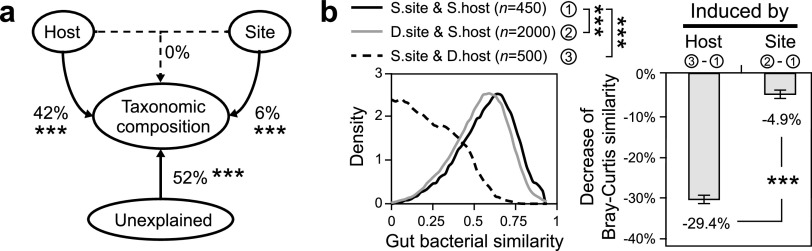
FIG 4.
Relative contribution of host species and geographical site to honeybee gut bacterial communities. (a) Variance partitioning analysis (VPA) revealed that host species had higher effects on gut bacterial communities than geographical site. (b) The variations of host species and geographical site decreased the similarities of honeybee gut bacterial communities, while the decrease induced by host species was significantly larger than by geographical site. Error bars were 95% confidence intervals. ***, P < 0.001.