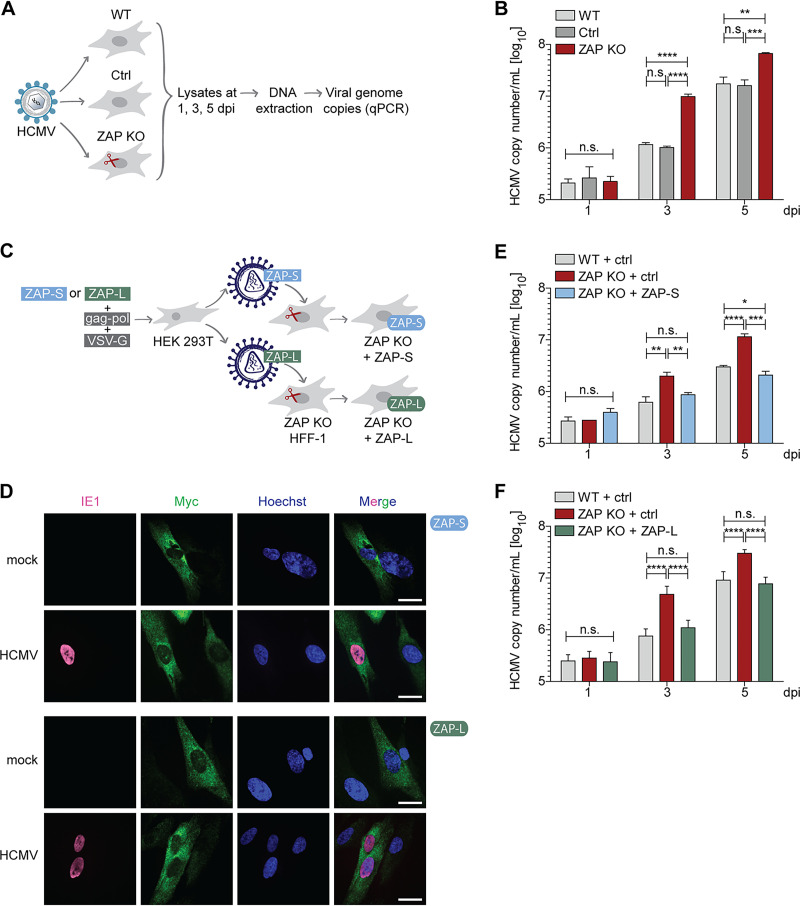
FIG 2.
ZAP-S and ZAP-L restrict HCMV replication in HFF-1 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the workflow to determine HCMV genome copy numbers. WT, control, or ZAP KO HFF-1 cells were infected with HCMV (MOI 0.1) for 2 h. Both cells and supernatant were harvested at 1, 3, and 5 days postinfection (dpi), followed by DNA extraction and measurement of viral genome copies by quantitative PCR. (B) HCMV genome copy numbers from WT, control, or ZAP KO HFF-1 cells were determined as described in panel A. HCMV copy numbers/ml are displayed as bar plots showing the mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) of biological triplicates. Results shown are one representative of at least three independent experiments using two different ZAP KO cell lines, with similar results obtained in all replicates. (C) Schematic representation of the workflow to reconstitute ZAP KO HFF-1 cells. HEK 293T cells were transfected with either myc-tagged ZAP-S or ZAP-L expression plasmids together with the packaging (gag-pol) and the envelope (VSV-G) plasmids to produce lentiviruses harboring ZAP-S or ZAP-L, respectively, followed by transduction of ZAP KO HFF-1 cells. As the control, WT and ZAP KO HFF-1 cells were transduced with lentiviruses harboring empty vector. (D) Subcellular localization of myc-tagged ZAP-S and ZAP-L in ZAP KO HFF-1 cells. ZAP KO cells were transduced as described in panel C with either myc-tagged ZAP-S or ZAP-L. Transduced cells were infected by centrifugal enhancement with HCMV (MOI 0.1), and 24 h postinfection, cells were fixed for immunolabeling with myc- and HCMV IE1-specific antibodies. IE1, immediate-early protein 1. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342. Scale bars represent 50 μm. (E and F) HCMV genome copy numbers from WT, ZAP KO, or ZAP KO HFF-1 cells reconstituted with ZAP-S (E) or ZAP-L (F) were determined as described in panel A. HCMV copy numbers/ml are displayed as bar plots showing the mean ± S.D. of one (E) or two combined independent (F) experiments performed with biological triplicates. Two independent experiments for both ZAP-S and ZAP-L were performed. Significant changes were calculated using unpaired two-sided Student’s t tests, n.s., not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.