FIG 3.
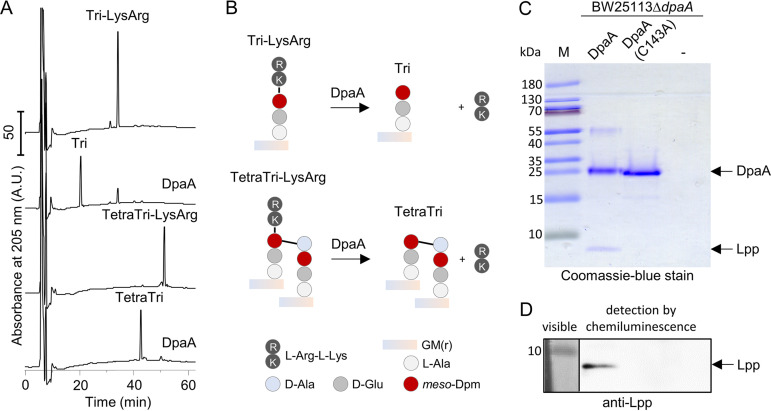
DpaA detaches Lpp from PG. (A) Activity against the muropeptides Tri-LysArg and TetraTri-LysArg. Muropeptides are the disaccharide peptide subunits released from PG by a muramidase. Tri-LysArg and TetraTri-LysArg (containing Lys-Arg from the C-terminus of Lpp) were incubated with DpaA, and the reaction products were reduced with sodium borohydride and separated by HPLC. DpaA hydrolyzed both substrates, releasing the muropeptides lacking l-Arg-l-Lys. The released dipeptide is missing in the chromatogram because it presumably coelutes early with the salts at ∼8 min. Table S2 shows the masses of the substrate and product muropeptides determined by mass spectrometry (MS). (B) Scheme of the reactions in panel A. Data in Fig. S1E show that LdtD and LdtE are not active against Tri-LysArg. Figure S2A and B show the inhibition of DpaA by copper. Muropeptide names are according to the work of Glauner et al. (14): Tri, disaccharide tripeptide; TetraTri, bis-disaccharide tetratripeptide. GM(r), N-acetylglucosamine-N-acetylmuramitol; l-Ala, l-alanine; l-Arg-l-Lys, l-arginyl-l-lysine dipeptide. (C and D) Lpp release assay. DpaA was incubated with PG sacculi from BW25113 ΔdpaA that were not treated with pronase E and hence contained PG-attached Lpp. Reaction mixtures were boiled and proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, following by staining with Coomassie-blue (C) or Western blotting and detection of Lpp with specific antiserum (D). DpaA, but not the catalytically inactive DpaA(C143A), released Lpp from PG. M, protein size marker.