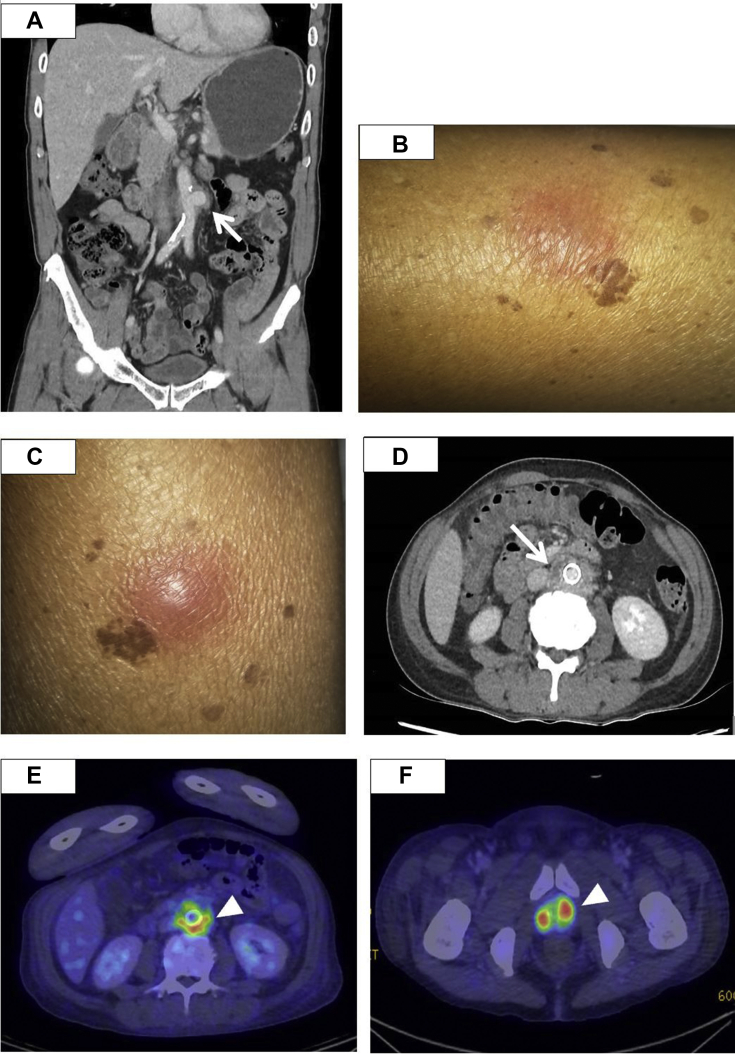
Fig 1.
A, Computed tomography (CT) urogram at initial presentation showing a saccular infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). The arrow points to the area suspicious for perianeurysmal fat stranding, for which the radiologist was concerned contained a leak of the aneurysm (arrow). B and C, Physical examination on postoperative day (POD) 54 revealed the presence of new subcutaneous raised nodules over the bilateral lower limbs, which was associated with a febrile illness, highly suggestive of a disseminated infection. D, Abdominal CT on POD 54 showed a new rim-enhancing collection adjacent to the endograft (arrow), most likely due to the endograft infection. Position emission tomography scans from POD 60 confirmed the diagnosis of aortic endograft infection, with fluorodeoxyglucose-avid uptake around the endograft (E) and prostate (F; arrowhead).