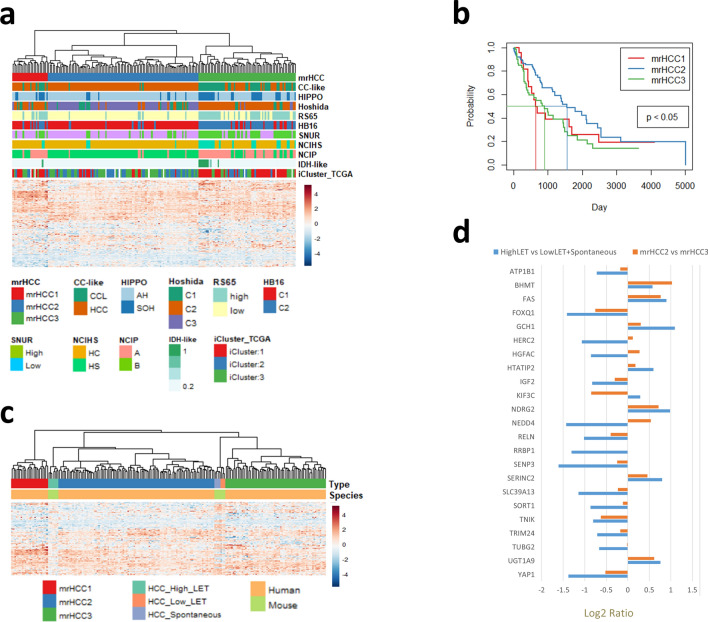
Figure 4.
The mR-HCC gene set derived from the mouse HCC model identified subgroups of the human TCGA HCC cohort. (a) Clustering analysis of TCGA HCC samples using log2 ratios of mR-HCC genes. The clustering defined 3 clusters: mrHCC1, mrHCC2, and mrHCC3. Rows of annotations under the dendrogram are overlaid with molecular subtypes previously published by TCGA. (b) Kaplan–Meier analysis in human HCC based on mrHCC clusters. The survival probability differed significantly (p < 0.05) across the three clusters, with patients in the mrHCC2 subgroup showing better survival. Straight lines indicate median survival time in each mrHCC subgroup. (c) Clustering analysis of integrated mouse and human expression data using mR-HCC genes. High-LET radiation-induced mouse HCC samples were clustered in mrHCC2; low-LET radiation-induced and spontaneous mouse HCC were clustered in mrHCC3. Heatmap was plotted using log2 radios of gene expressions between tumor and normal liver. (d) Comparison of averaged expression ratios using a subset of mR-HCC genes identified as related to HCC via data mining of the published literature. The mouse expression ratios were high-LET vs. low-LET/spontaneous HCC samples; the human expression ratios were mrHCC2 vs. human mrHCC3 samples.