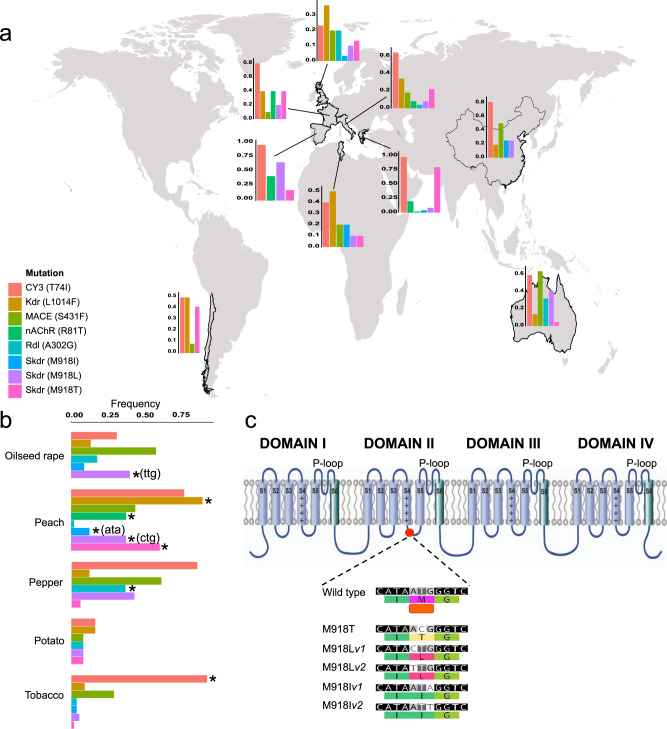
Fig. 5. Insecticide resistance mechanisms in global M. persicae.
a, b Frequency of eight resistance mutations in M. persicae collected from different countries (a) and host plants (b). Significant (p < 0.05) associations between specific resistance mutations and host-differentiated populations are denoted using a star (Fisher’s exact test). Significance applying to a specific codon is indicated in brackets. See Supplementary Data 1 for sample sizes. c Identification of novel resistance mutations in domain II of the voltage-gated sodium channel (VGSC) in M. persicae that confer resistance to pyrethroid insecticides. A schematic of the VGSC is shown above a nucleotide alignment illustrating the nature and position of two new mutations that both result in the same M918I substitution. For reference the wildtype sequence and the mutations leading to the amino acid substitutions reported previously at this position in resistant M. persicae are also displayed in the alignment.