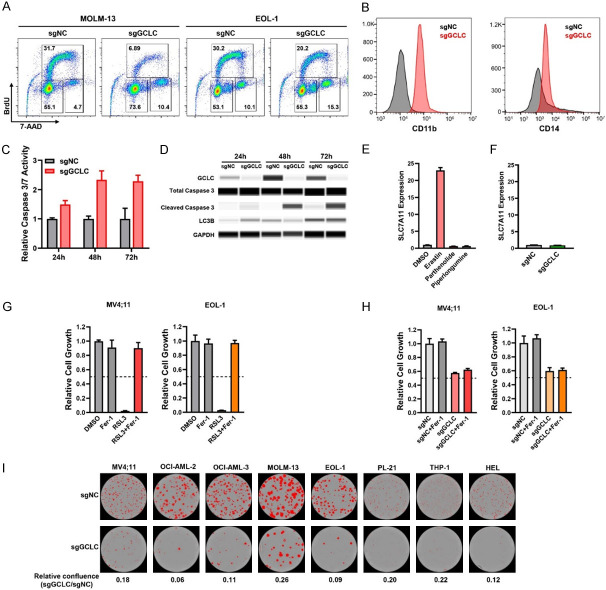
Figure 3.
Characterization of GCLC function in the regulation of cell cycle, cell differentiation, cell death and clonogenicity. (A) Effect of GCLC sgRNAs on cell cycle was determined by BrdU/7-AAD incorporation assays. (B) Expression levels of surface CD11b and CD14 in OCI-AML3 cells were assessed by flow cytometry following sgRNA-mediated GCLC knockout. (C, D) Effect of GCLC depletion by sgRNAs on apoptotic or autophagic cell death was detected by caspase 3/7 assay (C) and capillary Wes analysis with antibodies specific to cleaved caspase 3 or LC3B (D). EOL-1 cells were collected at time-points 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. (E) MV4;11 cells were treated with ferroptosis inducer Erastin and GCLC inhibitors Parthenolide and Piperlongumine for 24 h. Gene expression of SLC7A11 was determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and normalized to the level of β-ACTIN (ACTB). (F) MV4;11 cells were transduced with GCLC sgRNAs and the effect of GCLC depletion on SLC7A11 gene expression was determined by qPCR on day 3 with the normalization to ACTB level. (G) MV4;11 and EOL-1 cells were treated with ferroptosis inhibitor (1 µM Ferrostatin-1, Fer-1), GPX4 inhibitor (1 µM RSL3), or the combination. The effect on cell viability was determined after 24 h of incubation by CTG assay. (H) MV4;11 and EOL-1 cells were transduced with GCLC or control sgRNAs (sgGCLC or sgNC) for 48 h and Fer-1 was added to block ferroptosis for additional 24 h. The effect on cell growth was determined by CTG assay. (I) AML cell lines were transduced with sgGCLC or sgNC and plated in the methylcellulose media. The images of colonies and the quantification were determined by IncuCyte live-cell analyses.