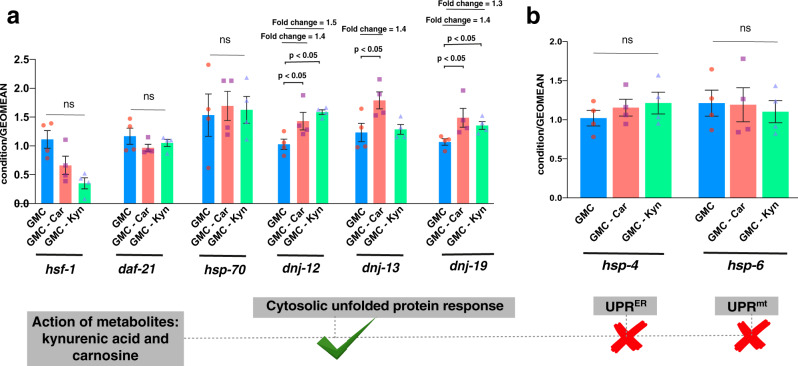
Fig. 6. RTqPCR shows that carnosine and kynurenic acid activate a cytosolic unfolded protein response by elevating the transcript levels of the J-proteins dnj-12 and dnj-19 in day 5 GMC worms.
GMC worms were administered 15 μM each of carnosine and kynurenic acid and their mRNA levels monitored by RTqPCR. a We did not observe any significant changes in the mRNA levels of hsf-1, hsp-90, and hsp-70. Carnosine treatment significantly elevated transcript levels of class A and B J-proteins, DNJ-12, DNJ-13, and DNJ-19. Kynurenic acid, however, elevated the levels only of class A J-proteins, DNJ-12, and DNJ-19. The changes in the transcript levels of J-proteins correlate to the protein level changes and are also supported by our RNAi knockdown experiments, where DNJ-13 does not show a role in clearing out the aggregates of Aβ42 aggregates (Fig. 8a, b). b We also tested for any changes in the UPRER and UPRmt after giving carnosine and kynurenic acid, however, found no significant changes in the markers, hsp-4 and hsp-6, corresponding to the activation of these pathways, respectively. All data represent four biological replicates of day 5 C. elegans GMC. Y-axis represents condition/GEOMEAN where condition refers to each hsf-1, daf-21, hsp-70, dnj-12, dnj-13, dnj-19, hsp-4, and hsp-6, and GEOMEAN is the geometric mean of two housekeeping genes rpb-2 and cdc-42 for normalization. We performed statistics using GraphPad Prism using one-way ANOVA with Tukey pairwise comparison of columns against the untreated GMC (AD) worms for each condition treated with metabolites. All error bars represent standard error of mean (SEM). Significance p-values are indicated above the bar plot. ns indicates statistically non-significant.