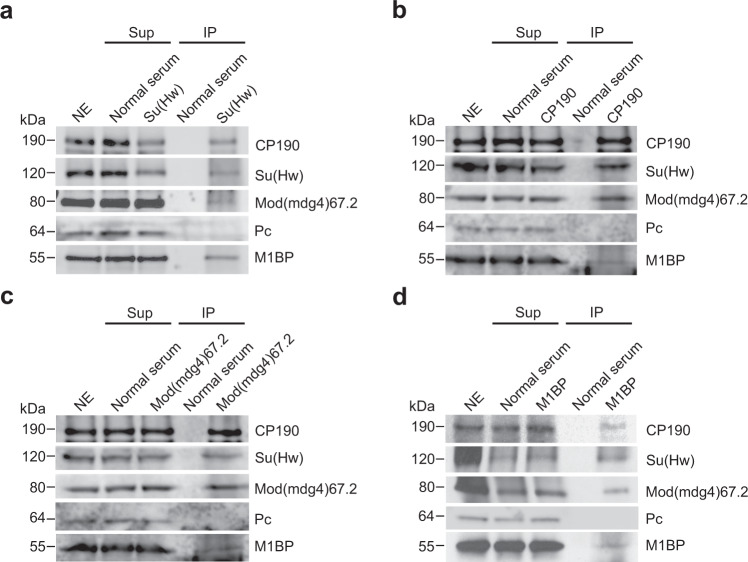
Fig. 1. Co-immunoprecipitation of core gypsy components with M1BP.
a Nuclear extracts (NE) from embryos aged 0–24 h were immunoprecipitated with either normal guinea pig serum or guinea pig anti-Su(Hw) antibody. Unbound supernatant (Sup) and bound (IP) fractions are shown. Polycomb (Pc) is shown as a negative control. In all, 10% of NE is loaded in the gel. We calculated that 5.2% of total CP190, 7.2% of Su(Hw), 1.9% of Mod(mdg4)67.2, and 5.3% of M1BP were immunoprecipitated with anti-Su(Hw) antibody. b Immunoprecipitation of M1BP with normal guinea pig serum or guinea pig anti-CP190 is shown. Overall, 12% of total CP190, 7.0% of Su(Hw), 8.2% of Mod(mdg4)67.2, and 3.8% of M1BP were immunoprecipitated with anti-CP190 antibody. c Immunoprecipitation of M1BP with normal rabbit serum or rabbit anti-Mod(mdg4)67.2 is shown. Overall, 11% of total CP190, 8.5% of Su(Hw), 10% of Mod(mdg4)67.2, and 3.0% of M1BP were immunoprecipitated with anti-Mod(mdg4)67.2 antibody. d Immunoprecipitation of M1BP with normal rabbit serum or rabbit anti-M1BP is shown. Overall, 3.8% of total CP190, 2.6% of Su(Hw), 1.4% of Mod(mdg4)67.2, and 3.7% of M1BP were immunoprecipitated with anti-M1BP antibody. Samples from the same experiment were run on different gels for proteins with similar molecular weights. All western blotting experiments were performed with at least two independent biological replicates for each antibody, and a single experiment is shown.