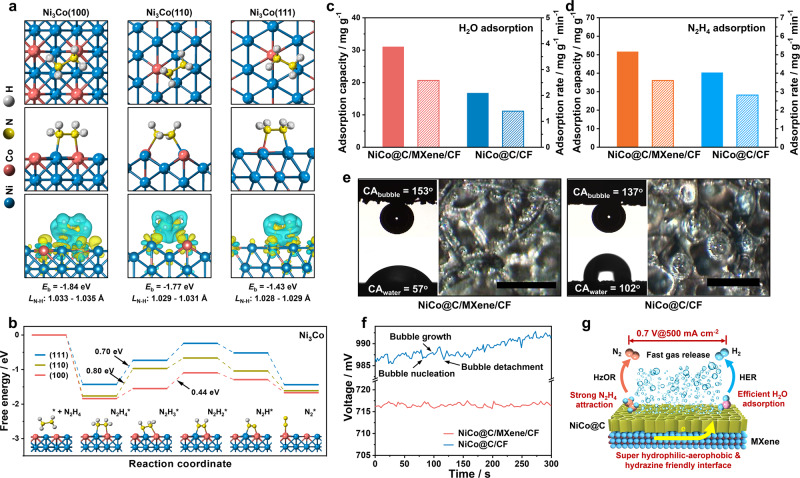
Fig. 6. Role of NiCo alloy and interfacial properties in promoting electrocatalytic performance.
a The structural model of N2H4 adsorption on various facets of Ni3Co alloy, and corresponding charge density difference analysis, where the yellow or cyan regions indicate the accumulation or depletion of the charge, respectively. The LN-H and Eb are the calculated N-H bond lengths (Å) and binding energy of the intermediates on Ni3Co alloy. b Free energy profiles of stepwise HzOR on different facets of Ni3Co alloy. Inset is the corresponding structural evolution of reaction intermediates adsorbed on the (100) facet of Ni3Co. Adsorption capability of (c) water or (d) hydrazine on NiCo@C/MXene or NiCo@C. e The contact angels of water (CAwater) and bubble (CAbubble) on NiCo@C/MXene/CF or NiCo@C/CF, and the optical images of gas bubbles released from both electrodes during HER. Scale bars: 500 μm. f Chronopotentiometric curves of NiCo@C/MXene/CF and NiCo@C/CF for hybrid seawater electrolysis. g Schematic illustration of the electrocatalytic enhancement of NiCo@C/MXene/CF at large current densities by overall enhancement in interfacial properties in terms of conductivity, robustness, water/hydrazine adsorption, and gas-releasing capability.