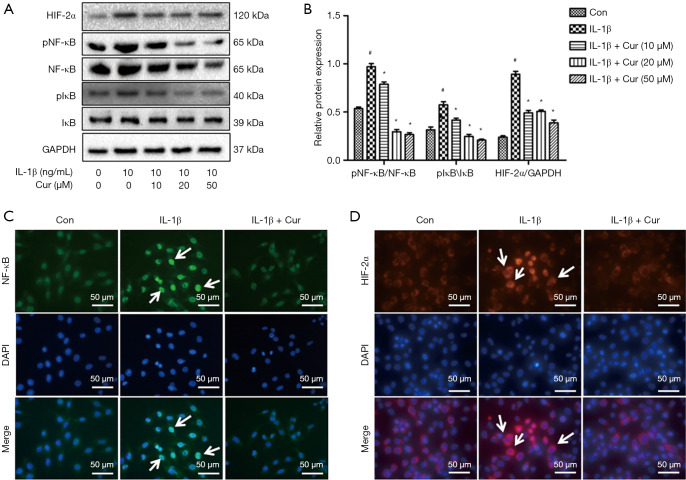
Figure 4.
The effects of curcumin on IL-1β-induced NF-κB/HIF-2α activation in mouse chondrocytes. (A) A representative Western blot showing the protein expression of HIF-2α, IκB-α, phosphorylated IκB-α, NF-κB, and phosphorylated NF-κB in chondrocytes. (B) A graphical representation of HIF-2α, IκB-α, phosphorylated IκB-α, NF-κB, and phosphorylated NF-κB protein expression normalized to GAPDH expression. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of NF-κB expression in the nucleus of chondrocytes. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of HIF-2α in the nucleus of chondrocytes. White arrows indicate NF-κB and HIF-2α positive cells in Figure 4C and 4D. Magnification 400×. #, P<0.05 vs. control group; *, P<0.05 vs. IL-1β group. Cur, curcumin; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; HIF-2α, hypoxia-inducible factor-2α; IκB-α, inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Con, control; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. White arrows indicate positive cells.