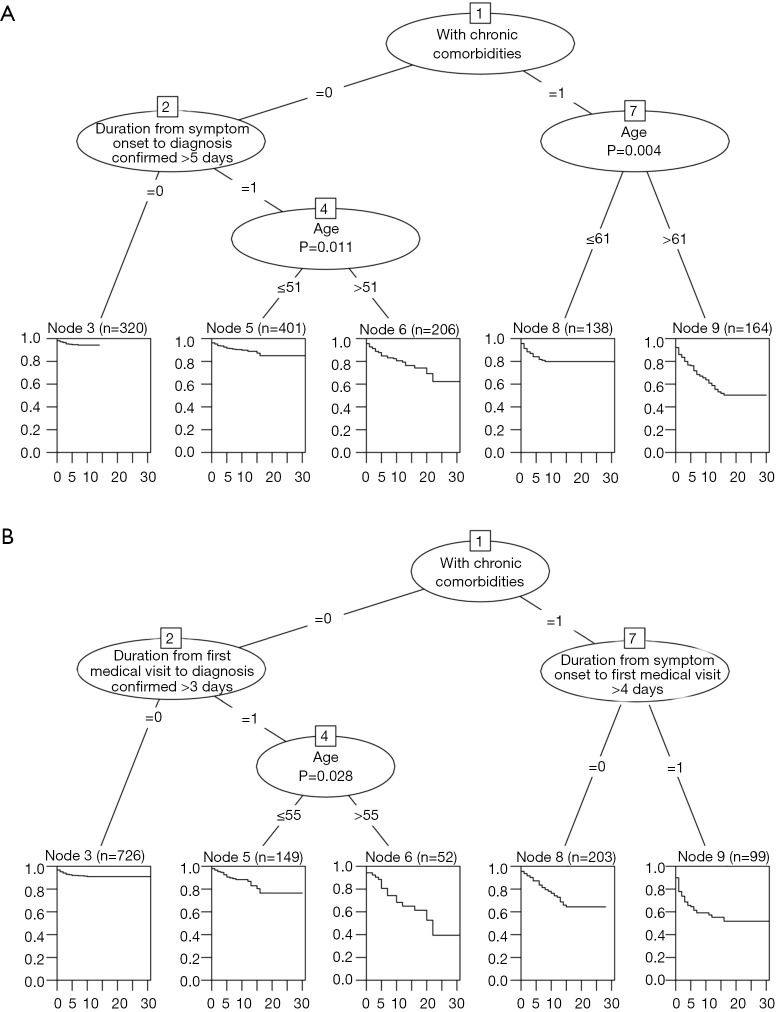
Figure 3.
Conditional inference tree models for COVID-19 prognosis with time from symptom onset to confirmed diagnosis and other prehospital factors. (A) The time-dependent risk of reaching a severe disease level divided into 5 sections according to the significantly separated nodes in the model tree; p values were calculated by the corresponding time series test (log-rank test); the model included duration from symptom onset to confirmed diagnosis, age, and chronic comorbidity status. (B) The time-dependent risk of reaching a severe disease level divided into 5 sections according to the significant separated nodes in the model tree; p values were calculated by corresponding time series test (log-rank test); the model included duration from symptom onset to first medical consultation, duration from first medical consultation to confirmed diagnosis, age, and chronic comorbidity status. The conditional inference tree (CTREE) recursively performs univariate splits of the dependent variable based on values on a set of covariates. CTREE tends to select variables that have many possible splits or many missing values using a significance test procedure to select variables instead of selecting the variable that maximizes an information measure (e.g., Gini coefficient).