Figure 3.
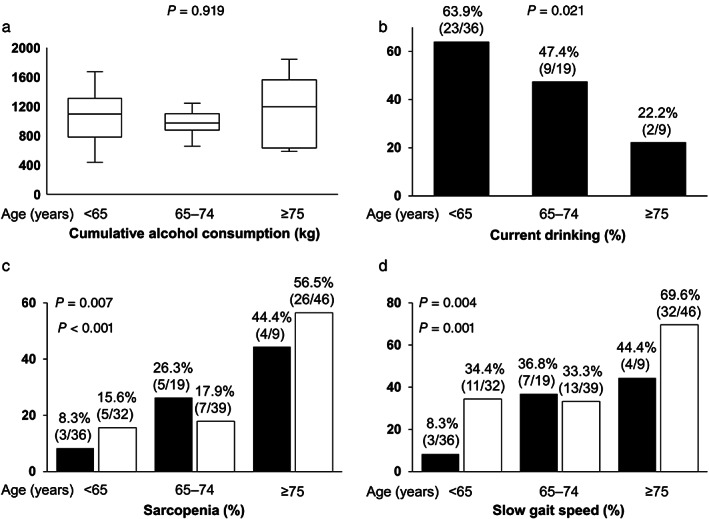
Comparison of alcohol consumption situations and the prevalence of sarcopenia and slow gait speed among the three age groups (<65, 65–74, and ≥75 years). (a) Cumulative alcohol consumption did not significantly differ among the three groups in the alcoholic liver cirrhosis (ALC) group (P = 0.919 by the Kruskal–Wallis test). (b) The prevalence of current drinking significantly decreased stepwise with advancing age in the ALC group (P = 0.021 by the Cochran–Armitage trend test). (c), (d) The prevalence of sarcopenia and slow gait speed increased stepwise with advancing age in the ALC group (P = 0.007 and 0.004, respectively, by the Cochran–Armitage trend test) and non‐ALC group (P < 0.001 and 0.001, respectively, by the Cochran–Armitage trend test). ( ), ALC; (
), ALC; ( ), non‐ALC.
), non‐ALC.
