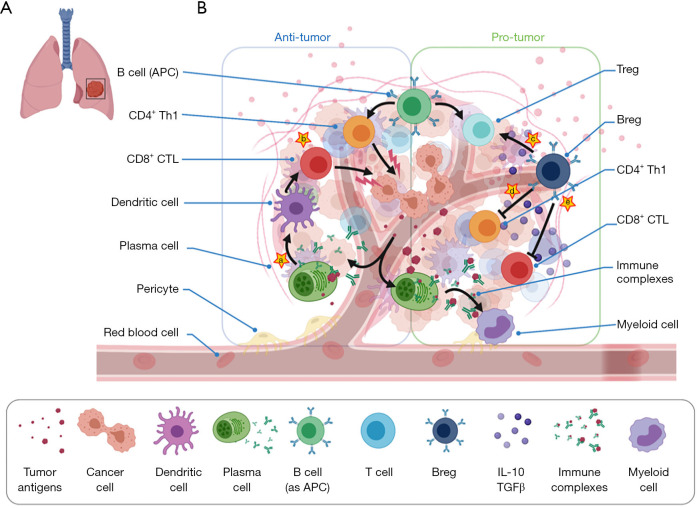
Figure 1.
The dual role of B cells in the lung cancer microenvironment. (A) Primary tumor in the left lung. (B) Tumor cells and TME. Anti-tumor activities are mediated via APC function and antibody production. Pro-tumor activities are mediated via production of pro-tumorigenic factors, activation of immunosuppressive T regulatory cells, and activation of myeloid-derived suppression cells. Pro-tumor activity is largely mediated by a specific subset of B regulatory cells. Sites for potential therapeutic targets are denoted yellow stars: (a) antigen-specific immunotherapeutic “vaccines” to induce B cell humoral response; (b) transfer of CD40 activated B cells that engage effector T cells; (c-e) specific inhibition of Bregs or IL-10. TME, tumor microenvironment; APC, antigen presenting cell; Th1, T helper type 1 cells; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; Treg, T regulatory cell; Breg, B regulatory cell.