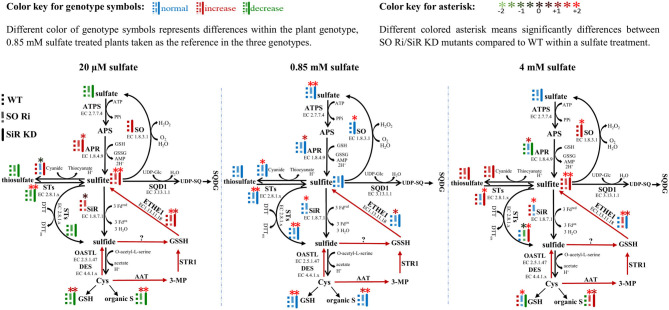
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration describing the impact of sulfite oxidase (SO) and sulfite reductase (SiR) impairment on the sulfur metabolism in Arabidopsis plants grown under sulfate starvation (20 μM), normal sulfate (0.85 mM), and excess sulfate (4 mM) levels as the only S source in 0.5 MS medium. Different color of genotype symbols represents differences within the plant genotype, 0.85 mM sulfate treated plants taken as the reference in the three genotypes (see above color key). Different colored asterisk means significant differences between SO Ri/SiR KD mutants compared with WT within a sulfate treatment (see above color key). The presented significant differences are based on statistical analyses shown in Figures 1, 2 and Supplemental Figure 1. The organic S was calculated as the difference between total S to the inorganic S (sulfate + sulfite). Red arrows indicate Cys catabolic pathway (Krüßel et al., 2014). ATPS, adenosine phosphate sulfurylase; APS, adenosine-5′-phosphosulfate; APR, APS reductase; SiR, sulfite reductase; STs, sulfur transferases; SQD1, UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase1; UDP-SQ, UDP-sulfoquinovose; SQDG, sulfolipid 6-sulfo-α-d-quinovosyl diacylglycerol; OAS-TL, O-acetyl-serine-thiol-lyase; SO, sulfite oxidase; Cys, cysteine; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; GSSH, glutathione persulfide; ETHE1, ethylmalonic encephalopathy protein1; DES, L-cysteine desulfhydrase; Fdox, Oxidized ferredoxin; Fdred, reduced ferredoxin; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; 3-MP, 3-mercaptopyruvate; AAT, aminotransferase; PPi, diphosphate; DTT, dithiothreitol; DTTox, Oxidized dithiothreitol.