Fig. 7. CASTAT5 potentiates the efficacy of CD19CAR T cell therapy in a murine B-cell lymphoma model.
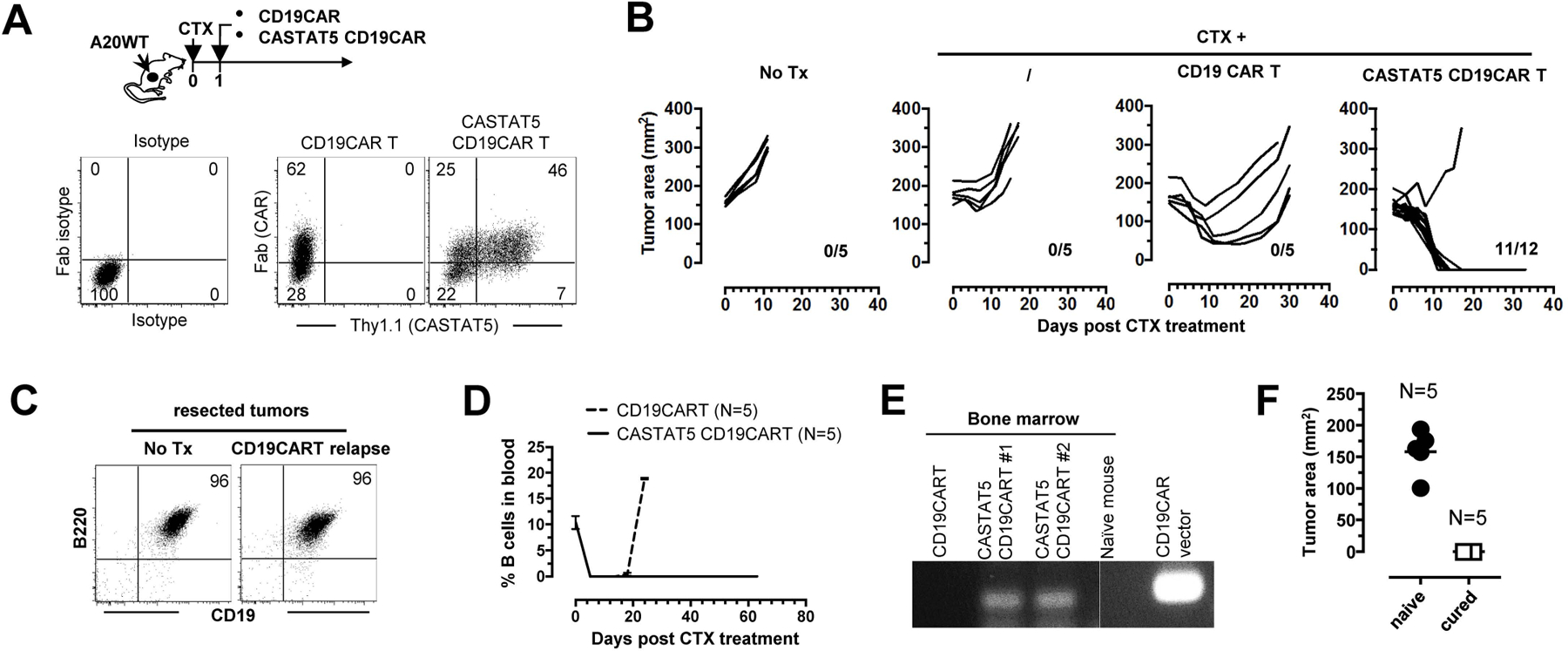
The schema depicts the timeline of the experimental procedures. A20WT tumor cells were subcutaneously inoculated to mice. When tumor sizes reached 170 mm2, mice were randomly grouped and received either no treatment (No Tx), CTX only, CTX + control CD19CAR T cells, or CTX + CASTAT5 CD19CAR T cells. (A) Expression of CAR and CASTAT5 in transduced T cells. Total T cells purified from CD45.1 mice were transduced to express CD19CAR alone or co-express CD19CAR and CASTAT5. Representative dot plots show the levels of CD19CAR and CASTAT5 in transduced T cells. CD19CAR was measured by anti-Fab stain and CASTAT5 was evaluated by Thy1.1 expression. (B) Tumor growth curves of each mouse under each condition are shown. The numbers indicate the number of tumor-free mice among treated mice at the end point. (C) Relapsed tumors did not lose CD19 expression. Mice treated with CD19CAR T cells had initial tumor regression followed by relapse. Relapsed tumors were resected and processed into single cell suspension for evaluation of CD19 expression by flow-cytometry. Tumors from untreated mice were used for comparison. Representative dot plots shown represent the co-stain of CD19 and B220. (D) Frequencies of host B cells in blood. At the indicated time points, tail blood was collected and the presence of host B cells in blood was evaluated by CD19 and B220 co-stain. (E) Detection of CD19CAR viral vector in bone marrow by PCR. 30 days after T cell transfer, a cohort of mice were killed and bone marrow aspirates were collected. The presence of CD19CAR T cells was evaluated by PCR detection of the CD19CAR viral vector. (F) Mice cured by CTX+CASTAT5 CD19CAR T cells were resistant to A20WT re-challenge. Live A20WT tumor cells were subcutaneously injected to cured mice and a group of naive mice used as controls. Tumor sizes in mice 3 weeks after tumor inoculation are shown.
