Figure 6.
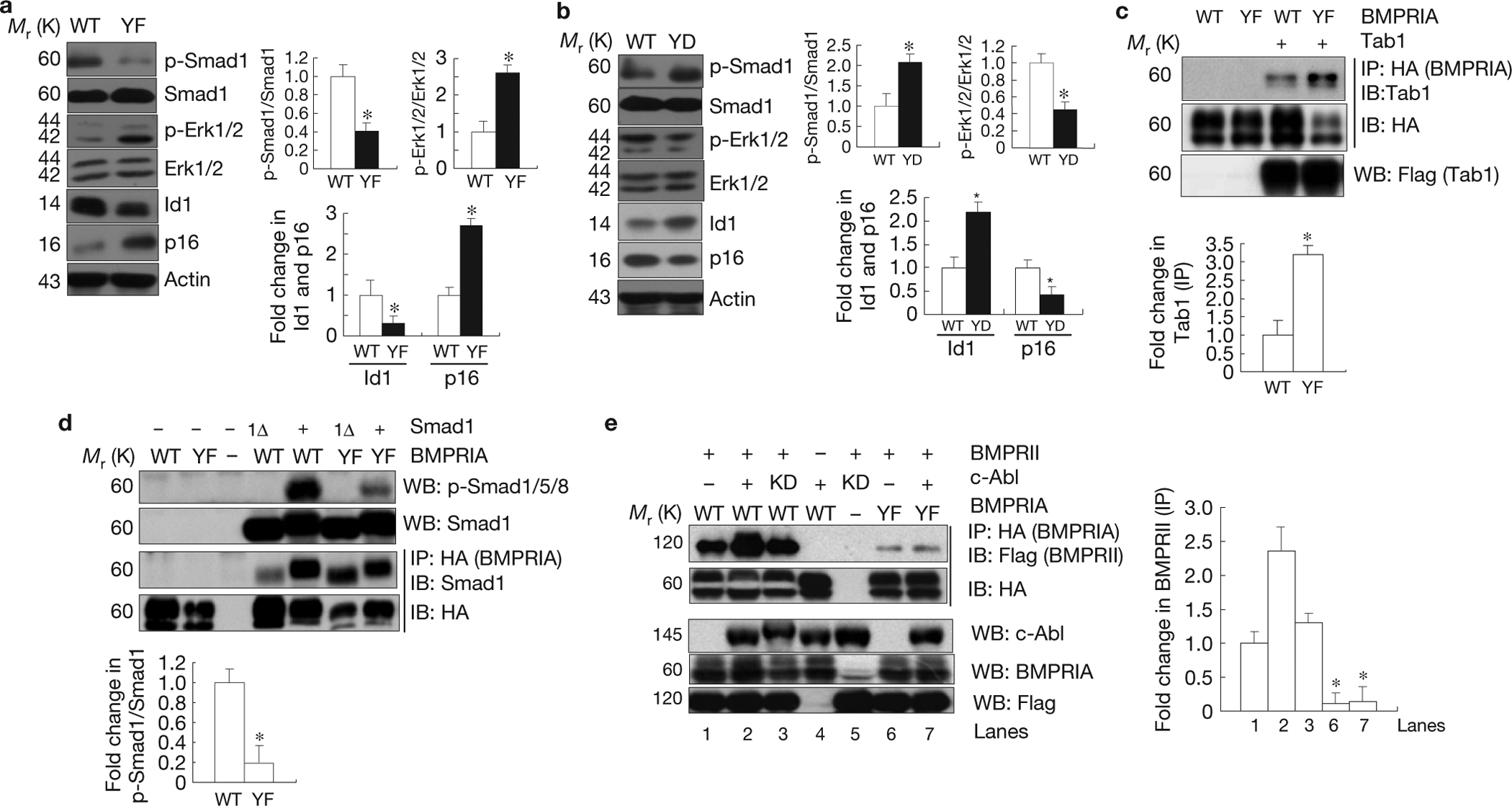
c-Abl-mediated BMPRIA phosphorylation negatively regulates Erk1/2 activation but positively regulates Smad1/5/8 activation. (a) Bmpr1a−/− osteoblasts expressing the mutant YF BMPRIA showed an increase in Erk1/2 activation and 16INK4a expression, but a decrease in Smad1 activation and Id1 expression. Right panel: quantification (fold change in p-Smad1/Smad1, p-Erk/Erk, Id1, and p16). (b) Bmpr1a−/− osteoblasts expressing YD mutant BMPRIA showed an increase in Smad1 activation and Id1 expression, but a decrease in Erk1/2 activation and p16INK4a expression. Right panel: quantification (fold change in p-Smad1/Smad1, p-Erk/Erk, Id1, and p16). (c) Enhanced interaction between mutant BMPRIA and Tab1. Mutant or WT BMPRIA was co-expressed with Tab1 in Cos7 cells cultured in normal medium. The mutant and normal BMPRIA were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies and the co-purified Tab1 was detected by western blot analysis. Lower panel: quantification. (d) The YF mutant BMPRIA had compromised activity in activating Smad1. The WT and YF BMPRIA were co-expressed with Smad1 or Smad1 carrying a deletion of the last 11 amino acids (Smad1Δ) in Cos7 cells cultured in normal medium. Western blot analysis was used to determine the activation of Smad1. The WT and YF BMPRIA were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies and the associated Smad1 was detected by anti-Smad1 antibodies. Lower panel: quantification. (e) c-Abl facilitated the interaction between BMPRII (Flag tagged) and BMPRIA. The WT and YF BMPRIA were co- expressed with BMPRII and c-Abl (or c-Abl KD) in Cos7 cells cultured in normal medium. BMPRIA was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies and the associated BMPRII was detected with an anti-Flag antibody. Right panel: quantification. Data are means ± s.e.m. (n = 3). *P < 0.05, compared with WT BMPRIA. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. S8.
