Figure 6.
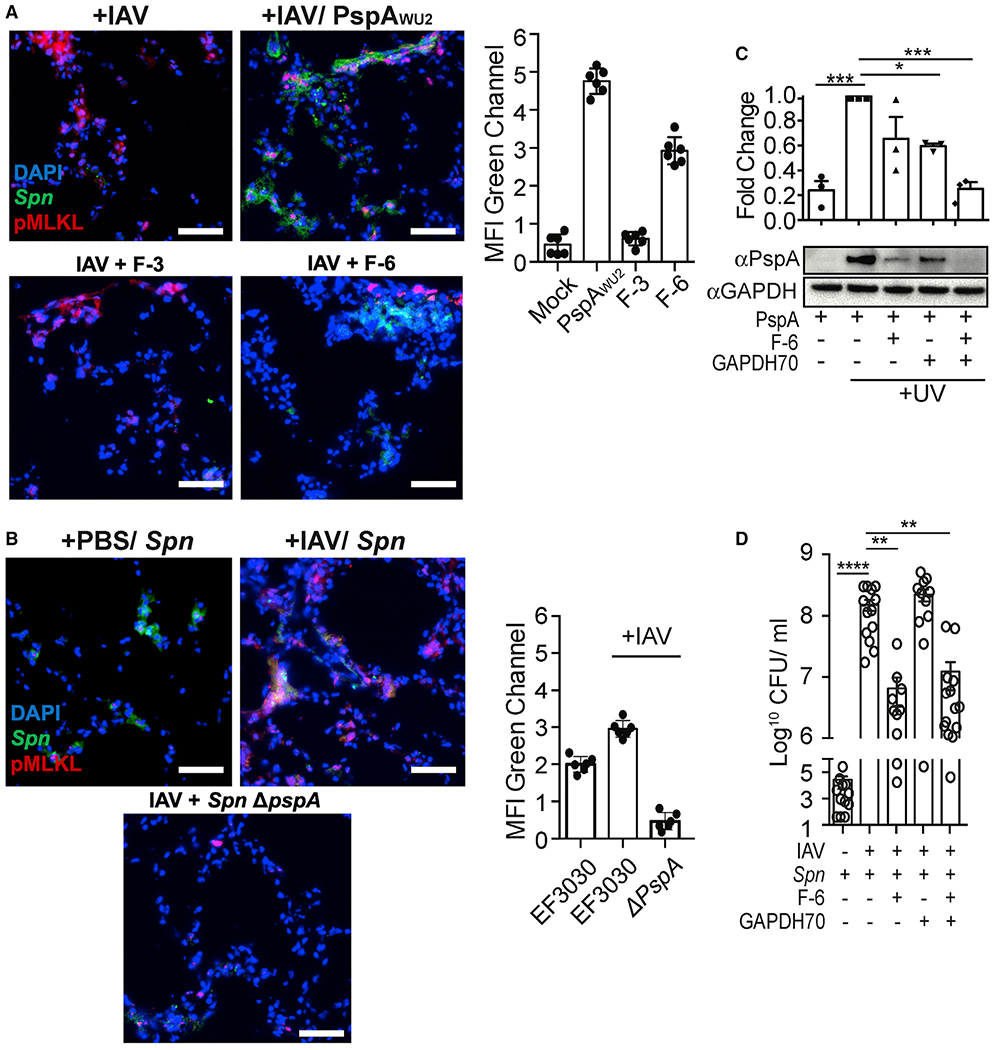
Spn binds influenza-mediated dying cells and induces pneumococcal superinfection
(A and B) Mice were challenged intratracheally with 200 PFUs of IAV (PR8) or saline (PBS) for 5 days and subsequently challenged intratracheally with (A) FITC-labeled whole rPspA, F3, and F6, or (B) infected with 106 CFUs of FITC-labeled Spn EF3030 (WT) or pspA isogenic mutant (Spn ΔpspA). One day after secondary challenge, lungs were collected andco-stained with anti-pMLKL (red) and DAPI (blue). MFI of the FITC-labeled (green) rPspA or adhered Spn was measured using ImageJ. Experiments were performed three times.
(C) UV-treated dying cells were incubated with GAPDH70 and subsequently with rPspA or F-6, and cell-bound PspA was assessed by immunoblot.
(D) Seven days following infection with IAV or control treated with PBS, mice were infected intratracheally with 107 CFUs of Spn EF3030 that had been mixed in suspension with F-6, GAPDH70, or F-6 with GAPDH70. The next day, Spn titers in whole-lung homogenates were determined. Open circles represent individual mice used for each experiment.
Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-comparison post-test. *p < 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.001. Scale bar: 50 μm for all microscopic images.
