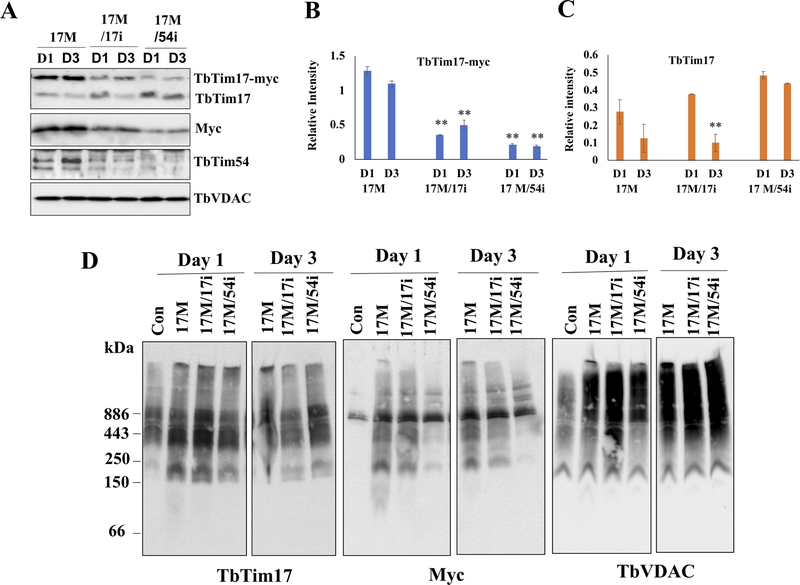
Figure 3|. Effect of TbTim54 KD on the import of TbTim17-Myc into mitochondria.
T. brucei cell lines TbTim17-Myc (17M), TbTim17-Myc/TbTim17-KD (17M/17i), and TbTim17-Myc/TbTim54-KD (17M/54i) were treated with doxycycline to simultaneously induce TbTim17-Myc expression and KD of TbTim17 and TbTim54, respectively. (A) On day 1 (D1) and day 3 (D3) post induction, cells were harvested to isolate their mitochondria. The mitochondrial samples were analyzed by immunoblot using antibodies for TbTim17, Myc, and TbTim54. VDAC served the loading control. Relative band intensity for TbTim17-Myc (B) and endogenous TbTim17 (C) were quantitated by densitometry and normalized to the intensities of the corresponding VDAC protein bands. Values shown are mean ± SEM from triplicate samples. ** P < 0.01, t-test in comparison to the 17M samples on day 1. (D) Analysis of mitochondrial protein complexes from wild type (con), 17M, 17M/17i, and 17M/54i cells. Mitochondrial proteins (100 μg) isolated at D1 and D3 post-induction were solubilized with digitonin (1.0%). The solubilized supernatant was clarified by centrifugation at 100,000 × g and analyzed by BN-PAGE. Protein complexes were detected by immunoblotting using antibodies for TbTim17, Myc and VDAC antibodies. Molecular size markers are shown. Blots are representatives of three independent experiments.