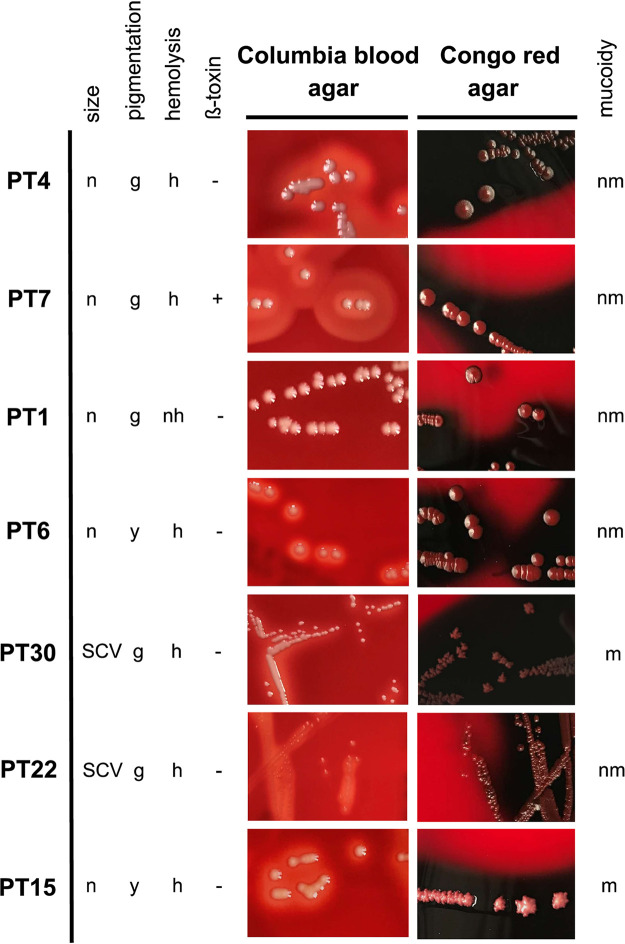
FIG 1.
Pictures of the seven most abundant phenotypes (PTs). S. aureus strains were cultured on Columbia blood agar and Congo red agar (CRA) plates and are characterized by the following parameters: size, mucoidy, hemolysis, β-toxin, and pigmentation. CRA was used to facilitate the discrimination of mucoid isolates. Special characteristics for mucoid isolates on CRA are a pyramidal-shaped morphology with rough wrinkled edges and a dry crystalline consistency (PT30 and -15), while nonmucoid isolates appear as flat and smooth colonies with a more moist consistency (PT4, -7, -1, -6, and -22). PT4 is normal (n), nonmucoid (nm), hemolytic (h), β-toxin negative (-), and gray (g). PT7 is normal, nonmucoid, hemolytic, β-toxin positive (+), and gray. PT1 is normal, nonmucoid, nonhemolytic (nh), β-toxin negative, and gray. PT6 is normal, nonmucoid, hemolytic, β-toxin negative, and yellow (y). PT30 is an SCV, mucoid (m), hemolytic, β-toxin negative, and gray. PT22 is an SCV, nonmucoid, hemolytic, β-toxin negative, and gray. PT15 is normal, mucoid, hemolytic, β-toxin negative, and yellow.