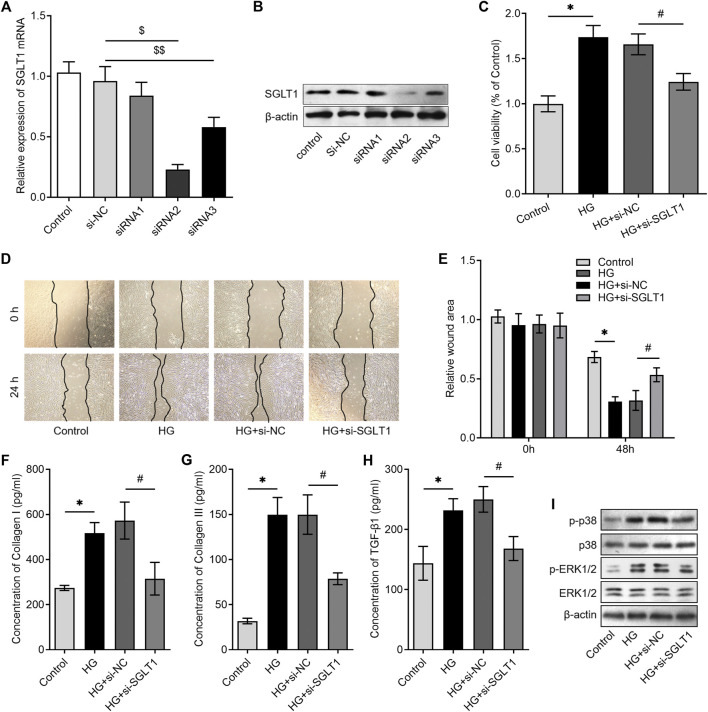
FIGURE 3.
Knockdown of SGLT1 inhibited high-glucose–induced CF activation. CFs were transfected with SGLT1 siRNAs, and SGLT1 mRNA and protein levels were detected using RT‐qPCR (A) and western blotting, respectively (B). CCK-8 assay was used to detect the proliferation of CFs under high-glucose condition with or without SGLT1 inhibition. (D, E) The representative images of the wound-healing assay were obtained at 0 and 24 h after knockdown of SGLT1, and the migrative ability of CFs was compared. (F–H) ELISA was used to detect the levels of collagen-synthesis–related markers, including TGF-β1, collagen I, and collagen III in the cell supernatant (n = 6). (I) Western blotting analysis was performed to investigate the phosphorylation levels of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 in CFs under high-glucose condition with or without SGLT1 inhibition.