FIGURE 1.
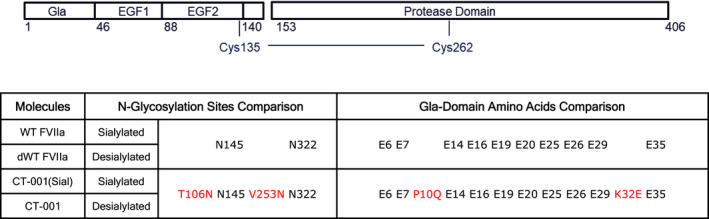
Structures of FVIIa variants. Wild‐type FVIIa (WT FVIIa) is composed of a Gla domain, 2 EGF domains, and a protease domain (PD). It is glycosylated with 2 N‐glycosylation sites (N145, N322). The N145 and N322 sites are composed of di‐ and triantennary carbohydrate chains with terminal GalNac capped with sialic acid. Highlighted in red are the amino acid substitutions relative to WT FVIIa. CT‐001(Sial) is engineered with P10Q and K32E in the Gla domain for enhanced affinity to negatively charged phospholipids and two additional N‐glycan structures T106 N and V253 N capped with sialic acid for providing a prolonged circulating half‐life to the molecule. CT‐001 is a desialylated variant of CT‐001(Sial) with additional terminal Gal and GalNAc moieties in comparison to dWT FVIIa to further accelerate plasma clearance and enhanced activity versus wild‐type sequences. dWT, desialylated wild‐type; EGF, epidermal growth factor; FVIIa, activated factor VII
