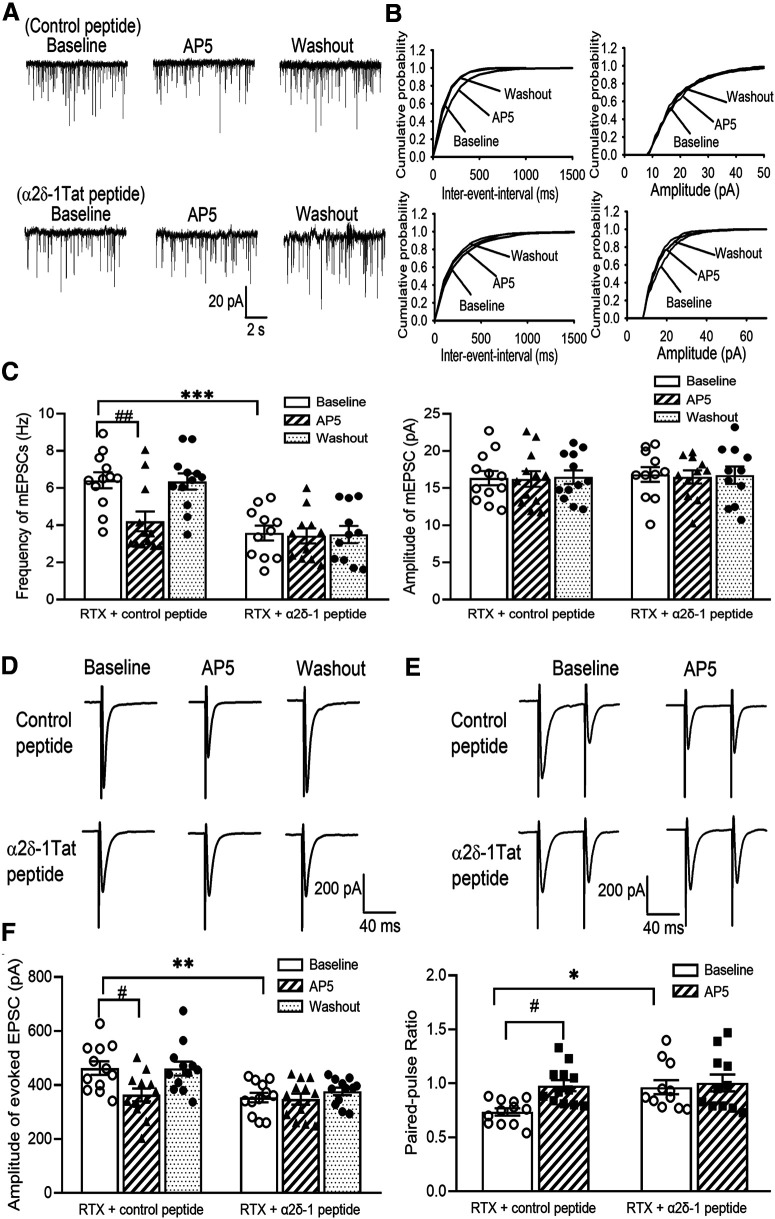
Figure 8.
Presynaptic α2δ-1–bound NMDARs mediate RTX-induced potentiation of glutamatergic input to spinal dorsal horn neurons. A, B, Original recording traces (A) and cumulative probability plots (B) show the effect of bath application of 50 μm AP-5 on mEPSCs of lamina II neurons from RTX-treated rats in which spinal cord slices were incubated with 1 μm control peptide or 1 μm α2δ-1Tat peptide. C, Mean data show the effect of AP-5 on the frequency and amplitude of mEPSCs of lamina II neurons from RTX-treated rats in which spinal cord slices were incubated with control peptide (n = 12 neurons) or α2δ-1Tat peptide (n = 11 neurons). D, E, Original recording traces show the effect of 50 μm AP-5 on evoked monosynaptic EPSCs (D) and paired-pulse evoked EPSCs (E) in lamina II neurons from RTX-treated rats from which spinal cord slices were incubated with 1 μm control peptide or 1 μm α2δ-1Tat peptide. F, Summary data show the effect of AP-5 on the amplitude of evoked EPSCs and the paired-pulse ratio in lamina II neurons from RTX-treated rats in which spinal cord slices were incubated with control peptide or α2δ-1Tat peptide (n = 12 neurons per group). Data are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with baseline in the control peptide group. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 compared with baseline before AP-5 application. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test.