Figure 1.
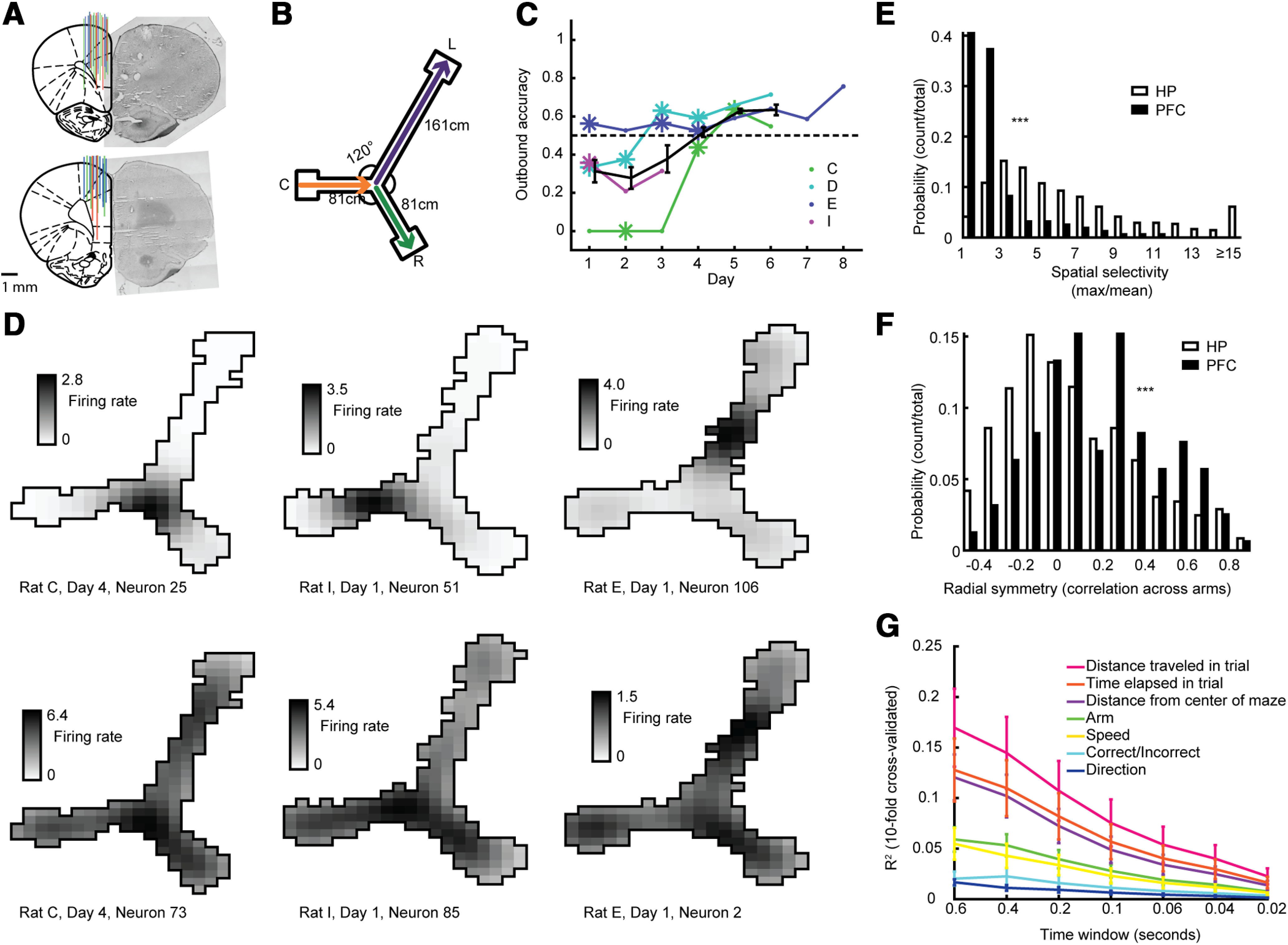
HP neurons were more modulated by the rat's position on the track than PFC neurons. A, PFC tetrode placement. Left, Summary of three rats, each with different color. Right, example histology images. B, Rats were rewarded for alternating between right and left arms, and always rewarded for returning to the center arm. C, Outbound accuracy in alternation task across days. Asterisks depict the 11 d from which neural recordings were used. Kendall's rank correlation between recording day and outbound accuracy, R = 0.56, p = 3.6e-4. D, top, Three examples of HP neurons recorded from three different rats showing place fields. Bottom, Three example prefrontal (PFC) neurons showing little spatial selectivity recorded simultaneously to the HP neurons in B. E, Spatial selectivity (max firing rate in binned position divided by the mean firing rate across bins) for all HP and PFC neurons. Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test, N = 158, 968, z = 5.36, p < 10−7. F, Radial symmetry (correlation across the three arms) for all HP and PFC neurons. Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test, N = 158, 968, z = −14.35, p < 10−45. G, Results from 10-fold cross-validated predictions of behavioral correlates using PFC neurons' firing rates.
