Figure 3.
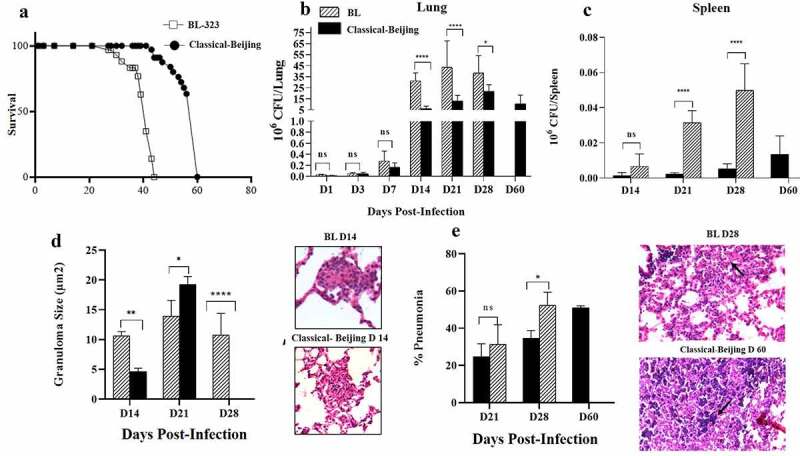
Survival, bacillary loads and histological changes in the lungs and spleen of BALB/c mice infected with Beijing strains. A). Survival of BALB/c mice infected by intratracheal injection of M. tuberculosis strains BL or Classical Beijing. B) Kinetics of bacillary loads in lungs infected with Beijing Strains. C). Bacterial burdens in the spleen, which indicate dissemination from lungs causing extrapulmonary TB. D) Granuloma size determined by automated morphometry and representative micrographs of granulomas (Black arrows) after two weeks of infection with the indicated strain. E) Percentage of lung surface affected by pneumonia (Black arrows strain BL day 28) determined by automated morphometry, and representative low-power micrographs of the lung from mouse infected after one month with strain BL, showing extensive areas of lung consolidation, and extensive pneumonia with areas of necrosis (Black arrows strain Classical Beijing day 60) in the lung of mouse after 2 months of infection with strain Classical Beijing. Multiple comparisons were performed using two-way ANOVA. Asterisks represent statistical significance * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.005, *** = P < 0.0005, **** = P < 0.0001 and n.s. Non-significant differences
