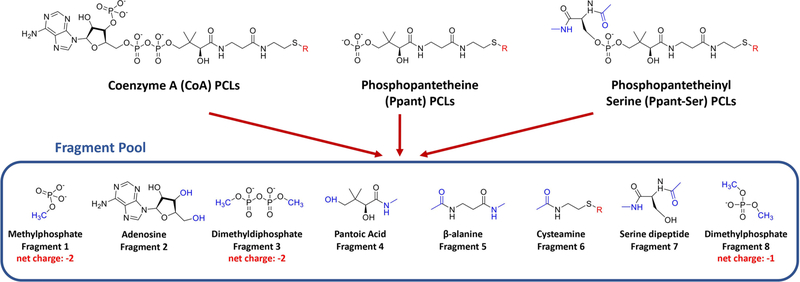
Figure 1.
“Plug-and-play” fragmentation strategy of PFF library development. Coenzyme A (CoA) PCLs, phosphopantetheine (Ppant) PCLs, and phosphopantetheinyl-serine (Ppant-Ser) PCLs can be fragmented into a fragment pool consisting of eight components: (1) methylphosphate, (2) adenosine, (3) dimethyldiphosphate, (4) pantoic acid, (5) beta-alanine, (6) cysteamine, (7) serine dipeptide, and (8) dimethylphosphate. CoA PCLs can be reconstructed with fragments 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6; Ppant PCLs can be reconstructed with fragments 1, 4, 5, and 6; Ppant-Ser PCLs can be reconstructed with fragments 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8. Various extending units that form thioester bonds with CoA, Ppant, or Ppant-Ser are labeled with “R” in red. Acetyl, methylamide, methyl, and hydroxyl caps that were constrained to 0 net charge and removed during the fragment merging process are depicted in blue.