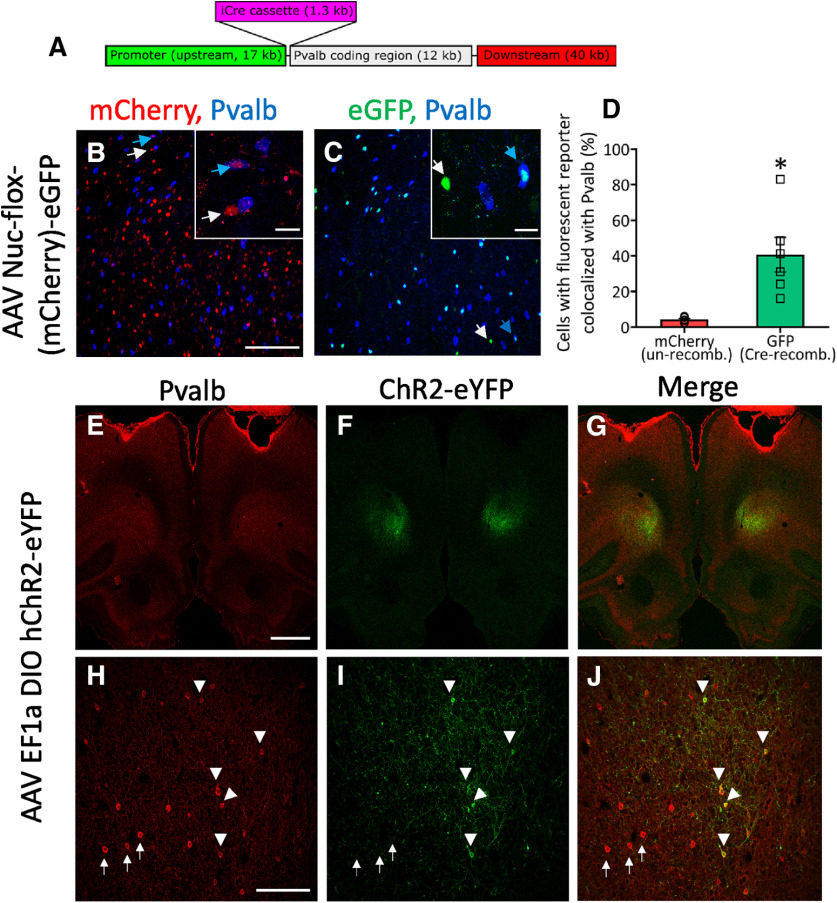
Figure 1.
Generation of Pvalb-Cre rats. A, Schematic of the Pvalb-iCre transgene produced by recombineering BAC CH230-499N20 which contains 17 kb of endogenous sequence upstream of the Pvalb start codon. Pvalb-iCre rats were injected bilaterally with AAV Nuc-flox-(mCherry)-eGFP into the OFC and brains processed for fluorescent imaging four weeks later. B, Unrecombined AAV genomes express mCherry in the OFC (red) and have minimal colocalization with Pvalb-positive cells (blue). Inset shows high magnification of a mCherry+, Pvalb+ cell (blue arrow), and a mCherry+, Pvalb– cell (white arrow). C, Cre-recombination leads to GFP-positive cells (Cre recombined; green) which showed colocalization with Pvalb (blue). Inset is high magnification example of a GFP+, Pvalb+ cell (blue arrow) and a GFP+, Pvalb– cell (white arrow). D, Quantitation of colocalization of mCherry (unrecombined) and GFP (Cre-recombined) with Pvalb-positive cells. *p = 0.038, paired t-test. E–J, Rats were injected with AAV EF1a DIO hChR2-eYFP and immunostained for parvalbumin 20 d later. At low magnifications, diffuse Pvalb-immunoreactivity (E) and focal ChR2-EYFP (F) expression in the OFC. At higher magnification, distinct Pvalb-immunopositive cells are present in OFC (H) and a mesh-like pattern of fluorescence from ChR2-EYFP expressed throughout cell bodies and processes in the OFC (I). In cells clearly exhibiting somal expression of ChR2-EYFP (white triangle), there is corresponding expression of Pvalb (J). Pvalb-positive cells that do not colocalize with ChR2-EYFP are indicated white arrow). Scale bars: 50 μm (B, C, H, J), 20 μm (inset), and 1000 μm (E–G).