Table 1.
Inhibitor activity of the test compounds (1–38) in the enol-keto and keto-enol tautomeric conversion of phenylpyruvate.
| Compounds | X | Ar | Inhibition of ketonase (IC50, μM) | Inhibition of enolase (IC50, μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | – | Phenyl | 82.8 ± 16.5 | 20.2 ± 3.9 |
| 2 | CH2 | Phenyl | 127 ± 20 | 113 ± 16 |
| 3 | (CH2)2 | Phenyl | 84.0 ± 15.3 | 129 ± 19 |
| 4 | CH2 | 4′- CH3-phenyl | 16.5 ± 3.4 | 2290 ± 343 |
| 5 | CH2 | 4′-OCH3-phenyl | 57.0 ± 14.1 | 33.4 ± 8.8 |
| 6 | CH2 | 4′-Cl-phenyl | 59.1 ± 9.7 | 42.8 ± 3.1 |
| 7 | CH2 | 2′-Cl-phenyl | 2640 ± 406 | 458 ± 73 |
| 8 | CH2 | 4′-Br-phenyl | 52.2 ± 11.5 | 232 ± 54 |
| 9 | CH2 | 3′-Br-phenyl | 7340 ± 1024 | 3350 ± 424 |
| 10 | CH2 | 4′-F-phenyl | 72.4 ± 3.4 | 42.1 ± 4.3 |
| 11 | CH2 | 2′,6′-(Cl)2-phenyl | 58.9 ± 10.3 | 35.5 ± 5.9 |
| 12 | CH2 | 3′,4′-(Cl)2-phenyl | 2620 ± 696 | 91.5 ± 9.0 |
| 13 | CH2 | 2′,4′-(Cl)2-phenyl | 16.9 ± 4.2 | 301 ± 42 |
| 14 | CH2 | 4′-COOH-phenyl | 187 ± 32 | 37.7 ± 16.3 |
| 15 | CH2 | 4′-(NCH3)2--phenyl | 90.2 ± 15.1 | 495 ± 101 |
| 16 | CH2 | 4′-CN-phenyl | 146 ± 17 | 43.2 ± 12.4 |
| 17 | CH2 | 3′,4′-(OCH3)2 -phenyl | 585 ± 94 | 302 ± 63 |
| 18 | CH2 | 3′,4′-(OCH2O)-phenyl | 50.7 ± 6.0 | 213 ± 31 |
| 19 | CH2 | 2′-Furyl | 57.7 ± 12.6 | 25.4 ± 4.7 |
| 20 | CH2 | 2′-Thienyl | 54.0 ± 5.5 | 52.3 ± 7.6 |
| 21 | CH2 | 2′-Pyrrolyl | 142 ± 31 | 125 ± 39 |
| 22 | CH2 | N-Methyl-2′-pyrrolyl | 23.8 ± 3.8 | 27.8 ± 5.6 |
| 23 | CH2 | 3′-Indolyl | 58.8 ± 10.6 | 2.89 ± 0.75 |
| 24 | CH2 | 2′-Pyridyl | 5.63 ± 0.94 | 28.6 ± 7.4 |
| 25 | CH2 | 3′-Pyridyl | 20.3 ± 5.5 | 28.6 ± 6.0 |
| 26 | CH2 | 4′-Pyridyl | 21.0 ± 6.9 | 209 ± 77 |
| 27 | O | Phenyl | 267 ± 59 | 1740 ± 483 |
| 28 | O | 4′- CH3-phenyl | 102 ± 19 | 3620 ± 829 |
| 29 | O | 3′- CH3-phenyl | 56.1 ± 8.8 | 443 ± 112 |
| 30 | O | 4′-OCH3-phenyl | 96.0 ± 29.9 | 425 ± 70 |
| 31 | O | 3′-OCH3-phenyl | 97.0 ± 20.7 | 205 ± 32 |
| 32 | O | 2′-OCH3-phenyl | 4.31 ± 1.34 | 1260 ± 159 |
| 33 | O | 4′-Br-phenyl | 311 ± 77 | 1890 ± 438 |
| 34 | O | 2′-Br-phenyl | 98.3 ± 16.0 | 3200 ± 887 |
| 35 | 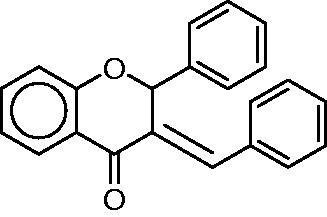 |
419 ± 113 | – (Because of low solubility data are not available) |
|
| 36 | S | Phenyl | 208 ± 42 | 633 ± 108 |
| 37 | SO | Phenyl | 94.6 ± 25.4 | 193 ± 59 |
| 38 | SO2 | Phenyl | 160 ± 38 | 151 ± 27 |
