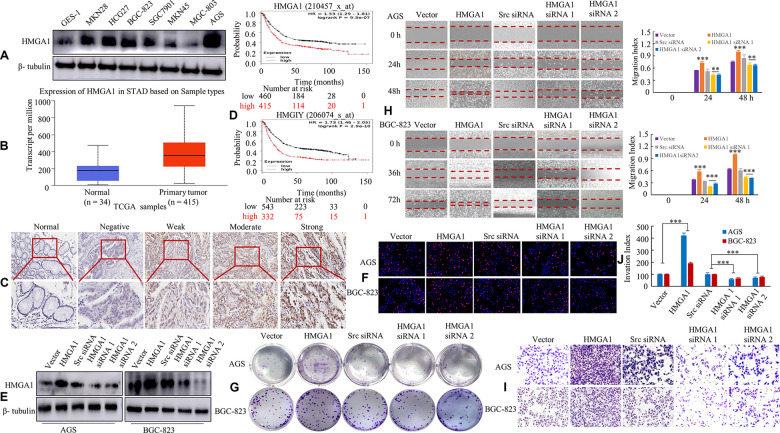
Figure 1.
HMGA1 expression is associated with the biological behavior of GC. (A) HMGA1 protein levels were assessed in GC cell lines and a human normal gastric epithelial cell line GES-1 using western blotting. β- tubulin was used as the internal control. (B) The protein expression of HMGA1 in GC and normal tissues analyzed by UALCAN cancer database. (C) IHC signal intensities were scored as nontumorous gastric mucosa (Normal), negative, weak, moderate and strong expression of HMGA1 protein in GC tissue. (D) OS survival curves of all GC patients cohorts (N = 875 and N = 875) from the KM plotter databases. N = number; OS, overall survival. (E) The protein levels of HMGA1 in AGS and BGC-823 cells with three treatments [Scrambled (Scr) siRNA, HMGA1 siRNA 1 and HMGA1 siRNA 2] determined by western blot analysis. (F) The GC cells transfected with the ectopic expression or knockdown of HMGA1 gene at 48 h and then stained with EdU and Hoechst 33342. (G) The AGS and BGC-823 cells were tested for the ability to form soft agar colonies. (H) Relative wound density at different time points of GC cells over a period of 48 h or 72 h. The measurements are from wounds made on a monolayer of GC cells cultured in the presence of different coating treatments and control. Original magnification, 10x. **, P < 0.05 and ***, P < 0.01. (I, J) In vitro the invasive ability of AGS and BGC-823 cells were evaluated by Transwell assay. The relative ratio of invasive cells was counted. ***, P < 0.01. Scale bars, 50 μm in (C); 100 μm in (F).