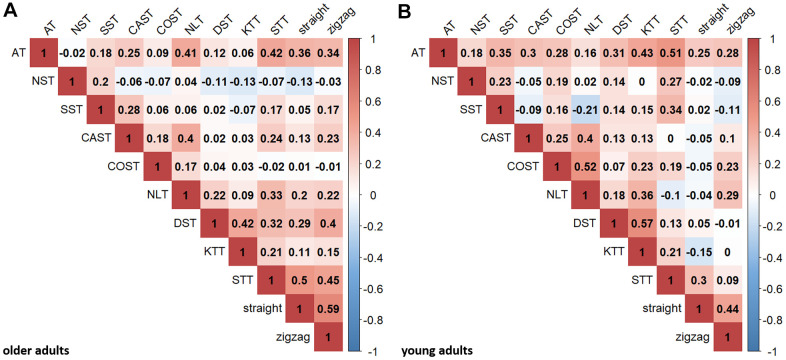
Figure 2.
Pearson correlations between executive and motor tasks. Pearson correlation coefficients are shown for older (A) and young (B) adults for descriptive purposes (critical r-value for p < .05, uncorrected: .205 (older adults), .389 (young adults); critical r-value for p < .000909, Bonferroni-corrected (.05/55): .341 (older adults), .612 (young adults)). AT, NST, SST represent inhibition; CAST, COST, NLT represent shifting; DST, KTT, STT represent updating. “straight” and “zigzag” indicate the respective BTT-conditions. All tasks were transformed so that higher scores indicate better performance.