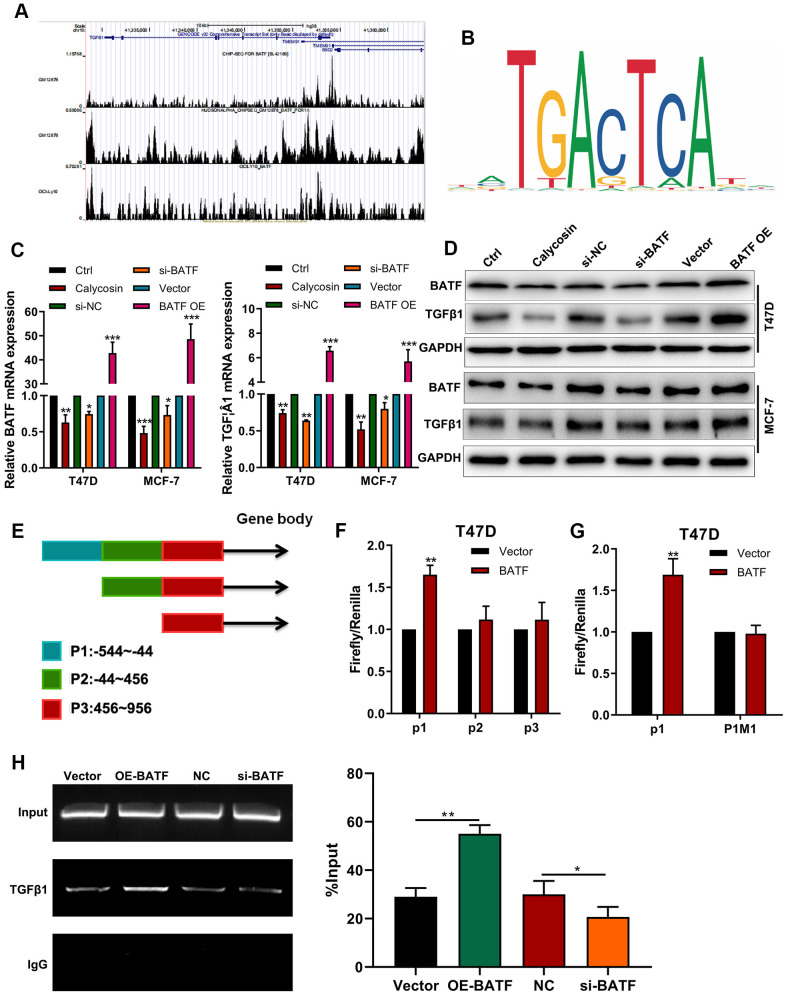
Figure 4.
Calycosin downregulates TGFβ1 expression via BATF. (A) ChIP-seq database analysis shows potential BATF binding sites in the TGFβ1 gene. (B) JASPAR database analysis shows potential BATF binding motif. (C) RT-qPCR analysis shows relative levels of BATF and TGFβ1 transcripts in calycosin-treated BATF-overexpressing, and BATF-knockdown T47D and MCF-7 cells and corresponding controls. (D) Western blot analysis shows relative levels of BATF and TGFβ1 proteins in control and calycosin-treated BATF-overexpressing and BATF-knockdown T47D and MCF-7 cells. (E) JASPAR database analysis shows 3 potential BATF binding sites in the promoter sequence of TGFβ1 gene (P1: -544~-44, P2: -44~456, P3: 456~956). (F) Dual-luciferase reporter assay results show relative luciferase activity in breast cancer cells transfected with luciferase reporter vectors containing P1, P2, or P3 promoter sequence of TGFβ1 gene. (G) Dual-luciferase reporter assay results show relative luciferase activity in breast cancer cells transfected with luciferase reporter vectors containing either wild-type P1 (P1 WT) or mutated P1 (P1 MUT) promoter sequence of TGFβ1 gene. (H) ChIP-PCR assay results confirm direct binding of BATF to TGFβ1. The data were represented as means ± SD. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.