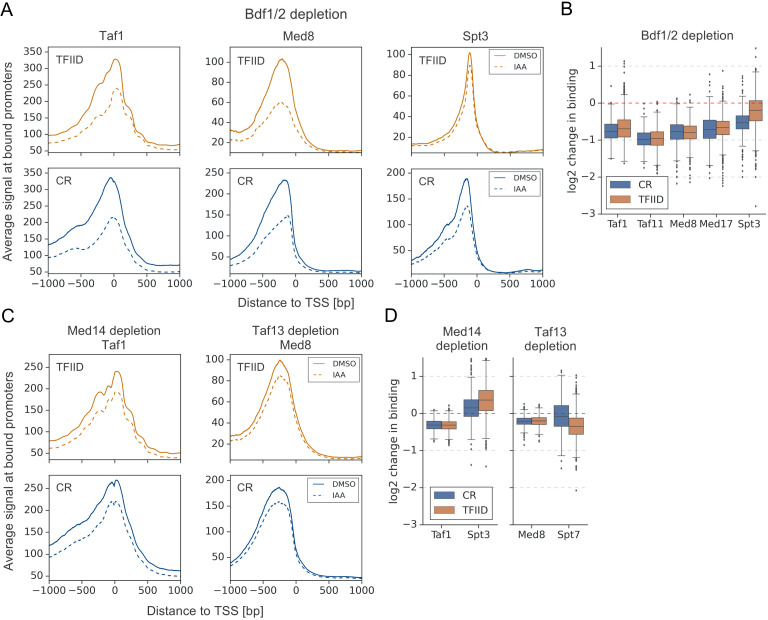
Figure 4. Bdf1/2 participate in recruitment of TFIID and Mediator to chromatin.
(A) Average plots comparing Taf1, Med8, and Spt3 ChEC-seq signals before (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO], solid line) and after (indole-3-acetic acid [IAA], dashed line) Bdf1/2 depletion at promoters bound by each factor and classified into TFIID-dependent and coactivator-redundant (CR) categories (2879, 890, and 2526 promoters, respectively). Mean values from replicate experiments are plotted. (B) Boxplot showing log2 change in promoter occupancy of indicated factors after Bdf1/2 depletion. Signals were calculated in a 200 bp window centered on a dominant peak. (C) Average plots comparing Taf1 and Med8 ChEC-seq signals before (DMSO, solid line) and after (IAA, dashed line) Med14 or Taf13 depletion, respectively. Same set of promoters as in (A) was used for this analysis. (D) Boxplot showing log2 change in promoter occupancy of indicated factors after Med14 or Taf13 depletion. Signals were calculated in a 200 bp window centered on a dominant peak. List of Spt3 bound promoters was used to calculate Spt7 occupancy. See also Supplementary file 3.