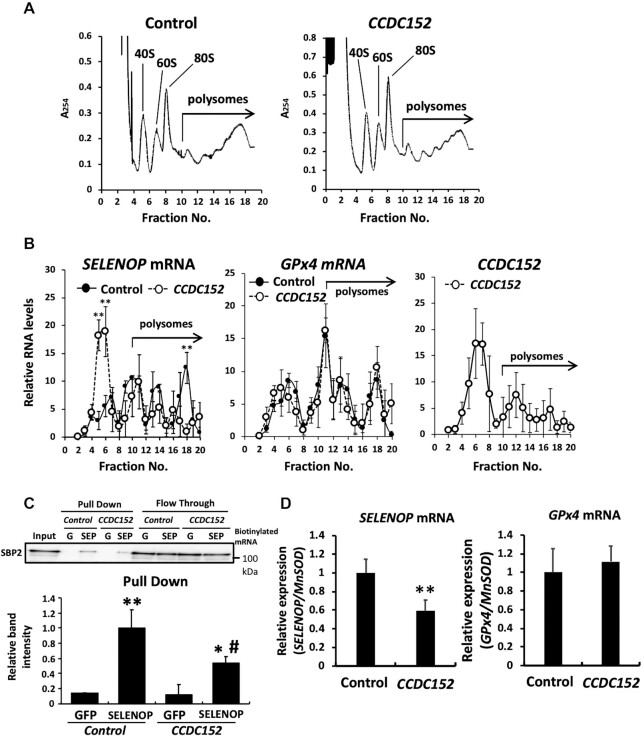
Figure 5.
Effects of the CCDC152 gene on the interaction between the SELENOP mRNA and ribosomes and the SBP2 protein. (A, B) Effects of CCDC152 gene transfection on total and SELENOP translation in HepG2 cells. The control and CCDC152 plasmids were transfected into HepG2 cells and the binding of ribosomes to total mRNA was determined by sucrose-gradient polysome analysis. Ribosome fractionation was revealed by measurement of absorbance at 254 nm (A254). Fractions 10 and 20 were assayed as polysomes (A). In the polysome analysis, the binding of ribosomes to the SELENOP mRNA, GPx4 mRNA, and CCDC152 RNA was determined. RNA in each fraction was extracted, its levels were measured and then a fixed volume of each RNA sample was subjected to quantitative PCR. The ratio of RNA levels in each fraction was calculated as the relative Ct value to total RNA (B, at least n = 3, mean ± SD). **P < 0.01 versus Control, Student's t test. (C, D) Effects of CCDC152 gene transfection on the interaction between the SELENOP mRNA and SBP2. The control and CCDC152 plasmids were transfected into HepG2 cells and whole-cell lysates were prepared. Biotinylated-GFP mRNA and SELENOP mRNA was added to each cell lysate and the binding of the SBP2 protein to each mRNA was evaluated (C). The precipitants were subjected to western blotting using an anti-SBP2 antibody, and the band intensity of SBP2 was evaluated (n = 3, mean ± SD). **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, versus GFP, #P < 0.05, versus SELENOP, control plasmid, Tukey-ANOVA. Anti-SBP2 Ab was added to each nuclear extracted fraction and the binding of the SELENOP and GPx4 mRNA to SBP2 was evaluated by the quantitative PCR (D). The MnSOD mRNA levels were used as a reference mRNA in the nuclear fraction (n = 3, mean ± SD). **P < 0.01 versus Control, Student's t test.