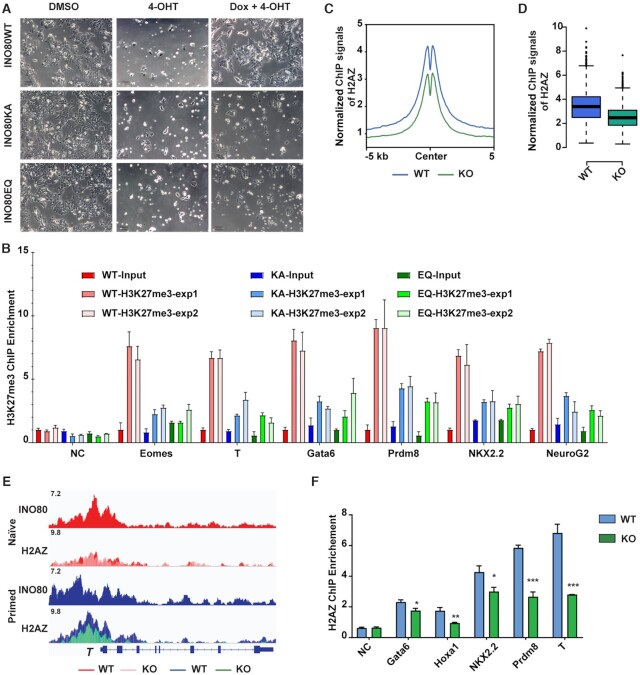
Figure 5.
INO80 promotes H2A.Z occupancy. (A) Rescue of Ino80 deletion phenotype by WT INO80 or INO80-ATPase-dead mutants. Ino80 deletion ESCs were transfected with the piggyBac vectors expressing Dox-inducible WT or ATPase-dead Ino80 (K551A, KA or E665Q, EQ). Ino80 deletion was induced by 4-OHT treatment and exogenous Ino80 expression was induced by Dox treatment simultaneously in serum/LIF. Cell morphology was imaged after one passage. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) ChIP-qPCR of H3K27me3 occupancy at selected bivalent promoters in Ino80 deletion cells expressing WT or ATPase-dead mutants during naïve to primed transition. Fold-enrichment was plotted as mean ± SEM. The experiment was repeated twice and shown as exp1 and exp2. (C, D) Normalized H2A.Z ChIP-seq signal at the INO80-bound bivalent promoters was examined by metagene (C) and violin (D) plots. Ino80 deletion ESCs were cultured in FAX and treated with DMSO or 4-OHT for 2 days and collected for ChIP-seq. (E) Genome browser view of INO80 and H2A.Z occupancy near T. (F) ChIP-qPCR to show H2A.Z occupancy at representative bivalent gene promoters in WT and Ino80 deletion cells. Fold-enrichment was plotted as mean ± SEM from three replicates. p-values were calculated by Student's t-test: * <0.05, ** <0.01, *** <0.001.