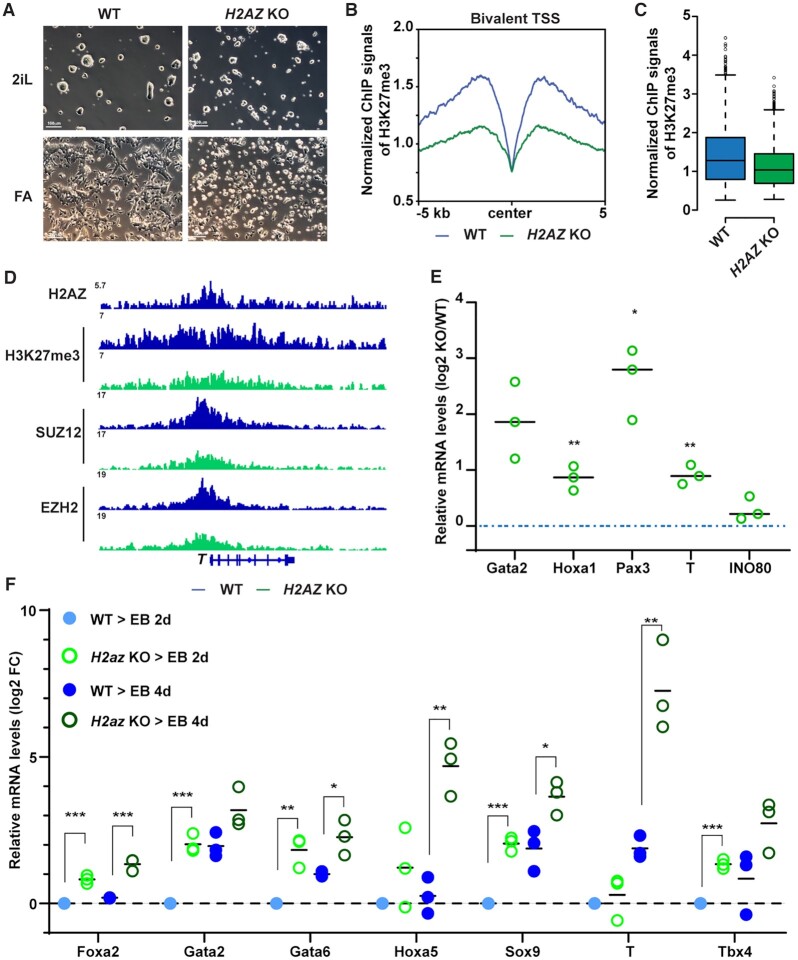
Figure 6.
INO80-dependent H2A.Z deposition licenses the establishment of bivalency. (A) H2az1/H2az2 deletion in the naïve state and during the naïve to primed transition. H2az1-cKO/H2az2-KO ESCs were cultured in the naïve state in 2iL and treated with DMSO or 4-OHT for 2 days. Cells were then maintained in the naïve state in 2iL or transitioned into FA for another 2 days to initiate the primed state. Cells were imaged and collected for ChIP-seq and RT-qPCR experiments. Scale bars = 100 μm. (B, C) H3K27me3 occupancy at INO80-bound bivalent TSSs in WT and H2az1/H2az2 deletion cells. Metagene and box plots were generated using normalized H3K27me3 ChIP-seq signals. (D) Genome browser view of H2A.Z, H3K4me3, H3K27me3, PRC2 component SUZ12 and EZH2 near T. (E) Expression of representative bivalent genes in WT and H2az1/H2az2 deletion cells. Relative mRNA levels were determined by RT-qPCR, first normalized to Gapdh and then normalized to wild-type cells, and log2 transformed. Scattered dots represent three independent experiments. p-values were calculated by Student's t-test: * <0.05, ** <0.01, *** <0.001. (F) Expression of representative bivalent genes in WT and H2az1/H2az2 deletion cells during EB formation. WT or H2az1/H2az2 deletion cells were induced to transition toward the primed state as described in A. Cells were aggregated to form EB for 2 and 4 days and collected for RT-qPCR. Expression of representative bivalent genes in wild-type and H2az1/H2az2 deletion ESCs and EBs was determined by RT-qPCR, first normalized to Gapdh and then normalized to wild-type EBs, and log2 transformed. Scattered dots represent three independent experiments. p-values were calculated by Student t-test: * <0.05, ** <0.01, *** <0.001.